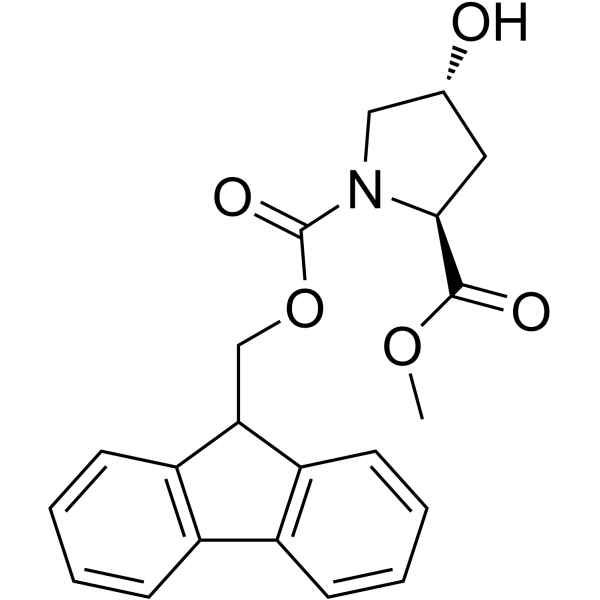
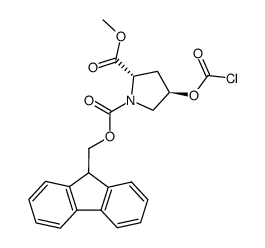
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH structure
|
Common Name | Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 187223-15-0 | Molecular Weight | 539.577 | |
| Density | 1.35±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 749.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H33N3O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 406.8±32.9 °C | |
Use of Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OHFmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH is a non-cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH is also a alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]< |
| Name | fmoc-l-hyp(bom)-oh |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH is a non-cleavable ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH is also a alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]< |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Cleavable |
| In Vitro | ADCs are comprised of an antibody to which is attached an ADC cytotoxin through an ADC linker[1]. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.35±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 749.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H33N3O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 539.577 |
| Flash Point | 406.8±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 539.226746 |
| PSA | 143.50000 |
| LogP | 3.54 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.620 |
| Water Solubility | Insuluble (1.5E-3 g/L) (25 ºC) |
|
~% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: NOVARTIS AG; NOVARTIS PHARMA GMBH Patent: WO2004/52817 A1, 2004 ; Location in patent: Page 19-20 ; |
|
~70% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: Lewis, Ian; Bauer, Wilfried; Albert, Rainer; Chandramouli, Nagarajan; Pless, Janos; Weckbecker, Gisbert; Bruns, Christian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 12 p. 2334 - 2344 |
|
~% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: Lewis, Ian; Bauer, Wilfried; Albert, Rainer; Chandramouli, Nagarajan; Pless, Janos; Weckbecker, Gisbert; Bruns, Christian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 12 p. 2334 - 2344 |
|
~% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: Lewis, Ian; Bauer, Wilfried; Albert, Rainer; Chandramouli, Nagarajan; Pless, Janos; Weckbecker, Gisbert; Bruns, Christian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 12 p. 2334 - 2344 |
|
~% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: Lewis, Ian; Bauer, Wilfried; Albert, Rainer; Chandramouli, Nagarajan; Pless, Janos; Weckbecker, Gisbert; Bruns, Christian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 12 p. 2334 - 2344 |
|
~% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: Lewis, Ian; Bauer, Wilfried; Albert, Rainer; Chandramouli, Nagarajan; Pless, Janos; Weckbecker, Gisbert; Bruns, Christian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 12 p. 2334 - 2344 |
|
~% 
Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH CAS#:187223-15-0 |
| Literature: Lewis, Ian; Bauer, Wilfried; Albert, Rainer; Chandramouli, Nagarajan; Pless, Janos; Weckbecker, Gisbert; Bruns, Christian Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 46, # 12 p. 2334 - 2344 |
| 1,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid, 4-[[[[2-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]ethyl]amino]carbonyl]oxy]-, 1-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethyl) ester, (2S,4R)- |
| 1-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-4-({[2-({[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}amino)ethyl]carbamoyl}oxy)proline |
| Fmoc-(2S,4R)-Pro(4-OCO-NH-CH2-CH2-NH-Boc)-OH |
| 1,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid, 4-[[[[2-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]ethyl]amino]carbonyl]oxy]-, 1-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethyl) ester |
| (4R)-1-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-4-({[2-({[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)oxy]carbonyl}amino)ethyl]carbamoyl}oxy)-L-proline |
| Fmoc-Hyp(Bcc)-OH |
| Fmoc-(2S,4R)-(4-OCO-NH-CH2-CH2-NH-Boc)-Pro-OH |
| (2S,4R)-4-[[[[2-[[(1,1-Dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]ethyl]amino]carbonyl]oxy]-1,2-pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid 1-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethyl) ester |
| Fmoc-Hyp(Bom)-OH |