Dicamba
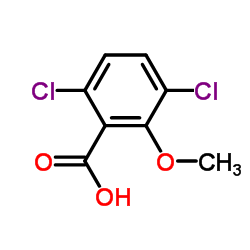
Dicamba structure
|
Common Name | Dicamba | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1918-00-9 | Molecular Weight | 221.037 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 326.1±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6Cl2O3 | Melting Point | 112-116 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 151.0±26.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | dicamba |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 326.1±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 112-116 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6Cl2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 221.037 |
| Flash Point | 151.0±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 219.969406 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 2.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.577 |
| InChIKey | IWEDIXLBFLAXBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1c(Cl)ccc(Cl)c1C(=O)O |
| Water Solubility | 50 g/100 mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H318-H412 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R41;R52/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S61-S36-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | DG7525000 |
| Hazard Class | 9.0 |
| HS Code | 2918990024 |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared ... |
|
|
Enhancing T-DNA Transfer Efficiency in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Cells Using Extracellular Cellulose and Lectin.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 176 , 1203-16, (2015) A major limitation of transforming barley tissues by Agrobacterium tumefaciens is the low frequency of T-DNA transfer due to recalcitrance of barley as a host. The effect of extracellular cellulose an... |
|
|
GH3 expression and IAA-amide synthetase activity in pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings are regulated by light, plant hormones and auxinic herbicides.
J. Plant Physiol. 170(4) , 361-8, (2013) The formation of auxin conjugates is one of the important regulatory mechanisms for modulating IAA action. Several auxin-responsive GH3 genes encode IAA-amide synthetases that are involved in the main... |
| banvel d |
| 3,6-dichloro-o-anisic acid |
| Banvel |
| Benzoic acid,2,4-dichloro-6-methoxy |
| cupric sulfate |
| Vanquish |
| 2,5-dichloro-6-methoxybenzoic acid |
| EINECS 217-635-6 |
| Benzoic acid, 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxy- |
| MFCD00055283 |
| 3,6-Dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid,3,6-Dichloro-o-anisic acid |
| 2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoic acid |
| Dicamba |
| 3,6-Dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid |
| disugran |
 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0 CAS#:3401-80-7
CAS#:3401-80-7 CAS#:6597-78-0
CAS#:6597-78-0 CAS#:90-01-7
CAS#:90-01-7 CAS#:10411-85-5
CAS#:10411-85-5
