Picloram
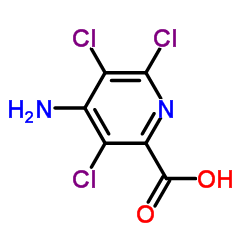
Picloram structure
|
Common Name | Picloram | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1918-02-1 | Molecular Weight | 241.459 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 420.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H3Cl3N2O2 | Melting Point | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 208.1±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of PicloramPicloram is an auxinic herbicide that is widely used for controlling broad leaf weeds[1]. |
| Name | picloram |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Picloram is an auxinic herbicide that is widely used for controlling broad leaf weeds[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 420.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H3Cl3N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 241.459 |
| Flash Point | 208.1±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 239.926010 |
| PSA | 76.21000 |
| LogP | 2.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.677 |
| InChIKey | NQQVFXUMIDALNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Nc1c(Cl)c(Cl)nc(C(=O)O)c1Cl |
| Water Solubility | 420 mg/L |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36:Irritating to the eyes. |
| Safety Phrases | S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | TJ7525000 |
|
~% 
Picloram CAS#:1918-02-1 |
| Literature: The Dow Chemical Company Patent: US4336384 A1, 1982 ; |
|
~91% 
Picloram CAS#:1918-02-1 |
| Literature: Litvineneko, G. S.; Ovchinnikov, V. G.; Lobanova, I. A.; Maksimenko, N. M.; Zatsarevnyi, V. M. J. Appl. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), 1992 , vol. 65, # 5 p. 1008 - 1016,824 - 830 |
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared ... |
|
|
Characterization of tub4(P287L) , a β-tubulin mutant, revealed new aspects of microtubule regulation in shade.
J. Integr. Plant Biol. 57 , 757-69, (2015) When sun plants, such as Arabidopsis thaliana, are under canopy shade, elongation of stems/petioles will be induced as one of the most prominent responses. Plant hormones mediate the elongation growth... |
|
|
GH3 expression and IAA-amide synthetase activity in pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings are regulated by light, plant hormones and auxinic herbicides.
J. Plant Physiol. 170(4) , 361-8, (2013) The formation of auxin conjugates is one of the important regulatory mechanisms for modulating IAA action. Several auxin-responsive GH3 genes encode IAA-amide synthetases that are involved in the main... |
| 4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid |
| 2-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 4-amino-3,5,6-trichloro- |
| Tordon |
| 4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic acid,4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid,Picloram |
| 4-Amino-3,5,6-trichlor-2-pyridinmethanol |
| MFCD00012101 |
| T6NJ BVQ CG DZ EG FG |
| Picolinic acid, 4-amino-3,5,6-trichloro- |
| 4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid |
| 3,5,6-trichloro-4-amino-picolinic acid |
| EINECS 217-636-1 |
| Picloram |
| 4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic Acid |
| 2-Pyridinemethanol,4-amino-3,5,6-trichloro |
| ATCP |
| Grazon |

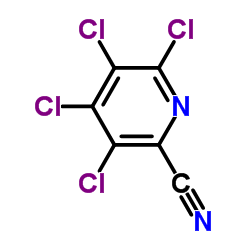
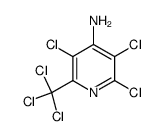
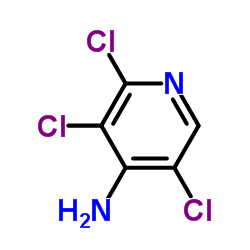
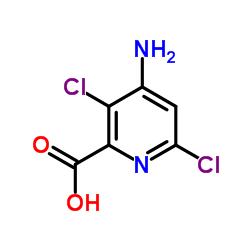 CAS#:150114-71-9
CAS#:150114-71-9 CAS#:100047-36-7
CAS#:100047-36-7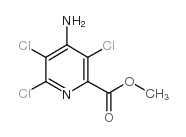 CAS#:14143-55-6
CAS#:14143-55-6
