| Description |
Ramelteon is a highly potent and selective melatonin receptor agonist with Ki values of 14 and 112 pM for human melatonin1 and melatonin2.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
IC50: 14 pM (melatonin1), 112 pM (melatonin2)[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Ramelteon shows very high affinity for human melatonin1 and melatonin2 receptors (expressed in CHO cells), and chick forebrain melatonin receptors (consisting of melatonin1 and melatonin2 receptors) with Ki values of 14.0, 112, and 23.1 pM, respectively. The affinity of ramelteon for hamster brain melatonin3 binding sites is extremely weak (Ki: 2.65 μM) compared to melatonin's affinity for the melatonin3 binding site Ki: 24.1 nM). In addition, ramelteon shows no measurable affinity for a large number of ligand binding sites (including benzodiazepine receptors, dopamine receptors, opiate receptors, ion channels, and transporters) and no effect on the activity of various enzymes. Ramelteon inhibits forskolin-stimulated cAMP production in the CHO cells that express the human melatonin1 and melatonin2 receptors[1].
|
| In Vivo |
Ramelteon significantly decreases wakefulness at doses of 0.001, 0.01, and 0.1 mg/kg, increases slow-wave sleep at doses of 0.001, 0.01, and 0.1 mg/kg, and increases rapid eye movement sleep at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg in freely moving cats[2]. Ramelteon is associated with reduced subjective sleep latency and improved sleep quality. Ramelteon is associated with improvement in latency to persistent sleep, sleep efficiency , and total sleep time[3]. Ramelteon (10 mg/kg, i/p), administered close to the mid-point of the dark phase of the L:D cycle, significantly reduces NREM sleep latency (time from injection to the appearance of NREM sleep). Ramelteon also produces a short-lasting increase in NREM sleep duration, but the NREM power spectrum is unaltered[4].
|
| Kinase Assay |
cDNA encoding the human MT1 gene is introduced into CHO cells. Cells are harvested at confluence in Ca2+ and Mg2+ free Hanks’ balanced salt solution containing 5 mM EDTA and collected by centrifugation. Cells are homogenized in ice-cold 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer, washed twice, pelleted, and stored at -30°C until the binding assays are conducted. Test compound and 40 pM 2-[ 125I]melatonin are mixed with the thawed homogenate in a total volume of 1 mL and incubated at 25°C for 150 min. The reaction is terminated by addition of 3 mL of icecold buffer followed by vacuum filtration on a Whatman GF/B. The filter is washed twice and radioactivity is counted by a g-counter[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Rats: Ramelteon is dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 200 mg/mL, and diluted 100-fold in physiological saline immediately before use. A different group of six implanted rats is given vehicle or ramelteon (10 mg/kg i.p.). The EEG and EMG are recorded for 1 hr before injection and then for a further 3.5 hr. All treatments are administered at 24:00 hr (near the mid-point of the dark phase of the L:D cycle) with a minimum of 72 hr separating injections in the same animal. Each rat receives both treatments in a fully randomized, balanced cross-over design reducing the number of animals needed in the study[4].
|
| References |
[1]. Kato K, et al. Neurochemical properties of ramelteon (TAK-375), a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist. Neuropharmacology. 2005 Feb;48(2):301-10. [2]. Miyamoto M, et al. The sleep-promoting action of ramelteon (TAK-375) in freely moving cats. Sleep. 2004 Nov 1;27(7):1319-25. [3]. Kuriyama A, et al. Ramelteon for the treatment of insomnia in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2014 Apr;15(4):385-92. [4]. Fisher SP, et al. Acute sleep-promoting action of the melatonin agonist, ramelteon, in the rat. J Pineal Res. 2008 Sep;45(2):125-32.
|
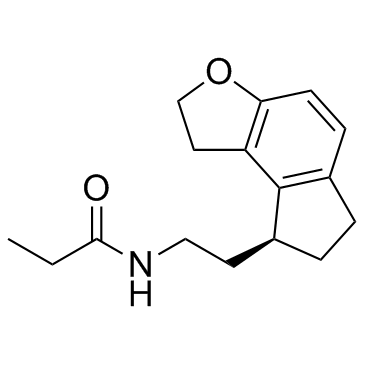




![(S)-2-(2,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)acetonitrile Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/324/1185516-79-3.png) CAS#:1185516-79-3
CAS#:1185516-79-3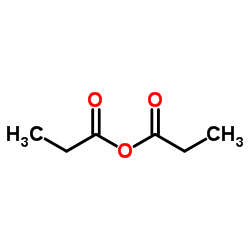 CAS#:123-62-6
CAS#:123-62-6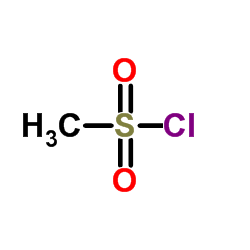 CAS#:124-63-0
CAS#:124-63-0![(S)-N-[2-[2,3-Dihydro-6-hydroxy-7-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1H-inden-1-yl]ethyl]propanamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/054/196597-88-3.png) CAS#:196597-88-3
CAS#:196597-88-3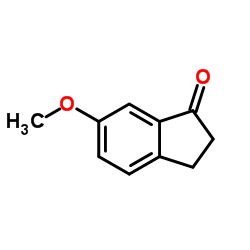 CAS#:13623-25-1
CAS#:13623-25-1 CAS#:187871-98-3
CAS#:187871-98-3 CAS#:178676-73-8
CAS#:178676-73-8![(E)-N-[2-(2,3-Dihydro-6-methoxy-1H-inden-1-ylidene)ethyl]propanamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/292/196597-82-7.png) CAS#:196597-82-7
CAS#:196597-82-7![(S)-N-[2-(5-Bromo-2,3-dihydro-6-hydroxy-1H-inden-1-yl)ethyl]propanamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/216/196597-84-9.png) CAS#:196597-84-9
CAS#:196597-84-9
