2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide
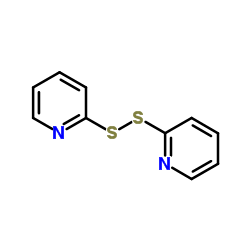
2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide structure
|
Common Name | 2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2127-03-9 | Molecular Weight | 220.31 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 356.1±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8N2S2 | Melting Point | 56-58 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 169.2±20.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide is a useful reagent for the determination of sulfhydryl groups. 2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide is a common reagent in peptide chemistry, often used in oxidation–reduction condensations to form peptide bonds or in coupling reactions to form disulfide-linked heterodimers[1]. |
| Name | 2-(pyridin-2-yldisulfanyl)pyridine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide is a useful reagent for the determination of sulfhydryl groups. 2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide is a common reagent in peptide chemistry, often used in oxidation–reduction condensations to form peptide bonds or in coupling reactions to form disulfide-linked heterodimers[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Formation of intramolecular S–S bonds can be dramatically accelerated by addition of a 2,2′-Dipyridyl disulfide (2-PDS) solution to an air-oxidized mixture of cysteine-containing peptides[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 356.1±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 56-58 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8N2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 220.31 |
| Flash Point | 169.2±20.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 220.012894 |
| PSA | 76.38000 |
| LogP | 2.53 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.694 |
| InChIKey | HAXFWIACAGNFHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | c1ccc(SSc2ccccn2)nc1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | 5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/22;R37 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37/39-S37/39-S25-S22 |
| RIDADR | UN3335 9 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Clay catalyzed RNA synthesis under Martian conditions: Application for Mars return samples.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 462 , 99-104, (2015) Catalysis by montmorillonites clay minerals is regarded as a feasible mechanism for the abiotic production and polymerization of key biomolecules on early Earth. We have investigated a montmorillonite... |
|
|
Development of an enzymatic assay system of D-lactate using D-lactate dehydrogenase and a UV-LED fluorescent spectrometer.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 116 , 150-5, (2015) In this study, we aimed to develop a new enzymatic assay system of d-lactate with good precision, accuracy, and sensitivity for the determination of D-lactate concentrations in rat serum. D-Lactate de... |
|
|
The RimL transacetylase provides resistance to translation inhibitor microcin C.
J. Bacteriol. 196(19) , 3377-85, (2014) Peptide-nucleotide antibiotic microcin C (McC) is produced by some Escherichia coli strains. Inside a sensitive cell, McC is processed, releasing a nonhydrolyzable analog of aspartyl-adenylate, which ... |
| di(2-pyridyl) disulfide |
| Bis(2-pyridinyl) disulfide |
| 2,2'-Dipyridyl disuldide |
| pyridyl disulfide |
| 2,2'-Dipyridyl disulfide |
| 2-Pyridinyl disulfide |
| 2,2'-DIHYDROXYDIPHENYLMETHANE |
| 2,2'-Dithiobispyridine |
| 1,2-Di(pyridin-2-yl)disulfane |
| 2-Pyridin-2-yldisulfanylpyridine |
| MFCD00006287 |
| EINECS 218-343-1 |
| 2,2‘-Dithiodipyridine |
| 2-Dipyridyl disulfide |
| Aldrithiol 2 |
| 2,2′-dipyridyldisulfide |
| bis-pyridin-2-yl-disulfide |
| pyridyldisulfide |
| 2,2'-Disulfanediyldipyridine |
| Aldrithiol |
| Bis(2-pyridyl) disulfide |
| 2,2′-dipyridyl disulfide |
| Pyridine, 2,2'-dithiobis- |
| Aldrithiol™-2 |
| 2,2'-dipyridinyl disulfide |
| 2,2'-Dithiodipyridine |
| 4,4′-dipyridyldisulfide |
 CAS#:2637-34-5
CAS#:2637-34-5 CAS#:7758-19-2
CAS#:7758-19-2 CAS#:109-04-6
CAS#:109-04-6 CAS#:108-86-1
CAS#:108-86-1 CAS#:122334-49-0
CAS#:122334-49-0 CAS#:292638-85-8
CAS#:292638-85-8 CAS#:73322-01-7
CAS#:73322-01-7 CAS#:76410-88-3
CAS#:76410-88-3 CAS#:10002-30-9
CAS#:10002-30-9 CAS#:4783-68-0
CAS#:4783-68-0 CAS#:91-60-1
CAS#:91-60-1 CAS#:24367-35-9
CAS#:24367-35-9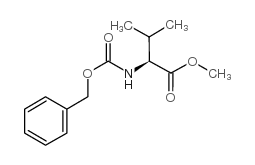 CAS#:24210-19-3
CAS#:24210-19-3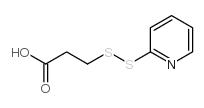 CAS#:68617-64-1
CAS#:68617-64-1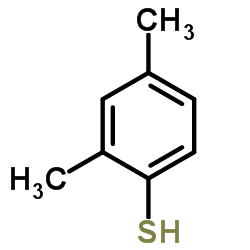 CAS#:13616-82-5
CAS#:13616-82-5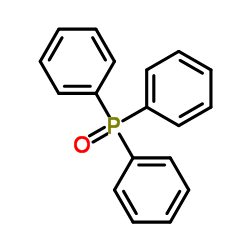 CAS#:791-28-6
CAS#:791-28-6 CAS#:106-54-7
CAS#:106-54-7
