2-di-1-asp
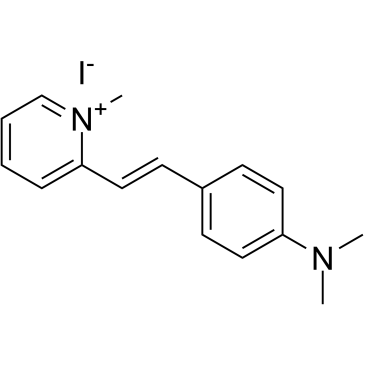
2-di-1-asp structure
|
Common Name | 2-di-1-asp | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2156-29-8 | Molecular Weight | 366.24000 | |
| Density | 1.091g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 397.8℃at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19IN2 | Melting Point | 280ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 179.3℃ | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2-di-1-asp2-Di-1-ASP (Compound 18a) is a mono-stryryl dye, and widely used as mitochondrial stain and groove-binding fluorescent probes for double-stranded DNA. 2-Di-1-ASP is selective for G-quadruplex (G4) and double-stranded DNA[1]. |
| Name | 2-[4-(dimethylamino)styryl]-1-methylpyridinium iodide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Di-1-ASP (Compound 18a) is a mono-stryryl dye, and widely used as mitochondrial stain and groove-binding fluorescent probes for double-stranded DNA. 2-Di-1-ASP is selective for G-quadruplex (G4) and double-stranded DNA[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 2-Di-1-ASP (Compound 18a) displays significant fluorescence enhancements in the presence of G-quadruplex (G4) structures (up to 300-fold), and good selectivity with respect to double-stranded DNA. 2-Di-1-ASP shows fluorimetric selectivity for parallel G4-DNA forms (c-kit2, c-kit87up, c-myc)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.091g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 397.8℃at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 280ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19IN2 |
| Molecular Weight | 366.24000 |
| Flash Point | 179.3℃ |
| Exact Mass | 366.05900 |
| PSA | 7.12000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.55E-06mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.668 |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
In silico activity profiling reveals the mechanism of action of antimalarials discovered in a high-throughput screen.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105 , 9059-64, (2008) The growing resistance to current first-line antimalarial drugs represents a major health challenge. To facilitate the discovery of new antimalarials, we have implemented an efficient and robust high-... |
|
|
Distribution pattern of viable mitochondria in bovine lens epithelial cells.
Dev. Ophthalmol. 26 , 90-6, (1994)
|
|
|
Live-cell imaging of the cytoskeleton and mitochondrial-cytoskeletal interactions in budding yeast.
Methods Mol. Biol. 586 , 41-68, (2009) This chapter describes labeling methods and optical approaches for live-cell imaging of the cytoskeleton and of a specific organelle-cytoskeleton interaction in budding yeast. |
| D-308 |
| 2-{2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]ethenyl}-1-methylpyridinium iodide |
| 2m2Pm |
| 2-(4-(Dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium |
| MFCD00011980 |
| o-DPD |
| 2-<4-(dimethylamino)styryl>-1-ethylpyridinium iodide |
| 2-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-1-methylpyridinium |
| (E)-2-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-1-methylpyridinium iodide |
| 2-(4-DIMETHYLAMINOSTYRYL)-1-METHYLPYRIDINIUM IODIDE |
| 2-DI-1-ASP |
| EINECS 218-460-8 |
| 1-METHYL-2-P-DIMETHYLAMINO-STYRYL-PYRIDINIUM-IODIDE |