Fludarabine
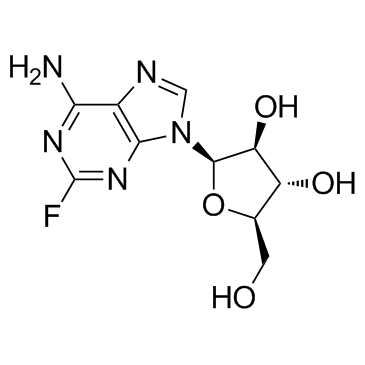
Fludarabine structure
|
Common Name | Fludarabine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21679-14-1 | Molecular Weight | 285.232 | |
| Density | 2.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 747.3±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12FN5O4 | Melting Point | 265-268ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 405.8±35.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of FludarabineFludarabine(NSC 118218), a DNA synthesis inhibitor, is a chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of hematological malignancies.Target:Fludarabine or fludarabine ph osphate (Fludara) is a chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of hematological malignancies (cancers of blood cells such as leukemias and lymphomas). It is a purine analog, which interferes with DNA synthesis. Fludarabine is highly effective in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, producing higher response rates than alkylating agents such as chlorambucil alone.Fludarabine is a purine analog, and can be given both orally and intravenously. Fludarabine inhibits DNA synthesis by interfering with ribonucleotide reductase and DNA polymerase. It is active against both dividing and resting cells. Being phosphorylated, fludarabine is ionized at physiologic pH and is effectually trapped in blood. This provides some level of specificity for blood cells, both cancerous and healthy. Fludarabine is associated with the development of severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a proportion of patients. Difficulties are often encountered when harvesting peripheral blood stem cells from patients previously treated with fludarabine. |
| Name | (2R,3S,4S,5R)-2-(6-amino-2-fluoropurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fludarabine(NSC 118218), a DNA synthesis inhibitor, is a chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of hematological malignancies.Target:Fludarabine or fludarabine ph osphate (Fludara) is a chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of hematological malignancies (cancers of blood cells such as leukemias and lymphomas). It is a purine analog, which interferes with DNA synthesis. Fludarabine is highly effective in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, producing higher response rates than alkylating agents such as chlorambucil alone.Fludarabine is a purine analog, and can be given both orally and intravenously. Fludarabine inhibits DNA synthesis by interfering with ribonucleotide reductase and DNA polymerase. It is active against both dividing and resting cells. Being phosphorylated, fludarabine is ionized at physiologic pH and is effectually trapped in blood. This provides some level of specificity for blood cells, both cancerous and healthy. Fludarabine is associated with the development of severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a proportion of patients. Difficulties are often encountered when harvesting peripheral blood stem cells from patients previously treated with fludarabine. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 2.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 747.3±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 265-268ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12FN5O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 285.232 |
| Flash Point | 405.8±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 285.087341 |
| PSA | 139.54000 |
| LogP | -0.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.876 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMF: 20 mg/mL, clear, faintly yellow |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R36/37/38;R39 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AU6207000 |
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared ... |
|
|
Trend analysis of a database of intravenous pharmacokinetic parameters in humans for 670 drug compounds.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 36 , 1385-405, (2008) We present herein a compilation and trend analysis of human i.v. pharmacokinetic data on 670 drugs representing, to our knowledge, the largest publicly available set of human clinical pharmacokinetic ... |
| UNII-P2K93U8740 |
| 9-b-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoro-9H-purin-6-amine |
| 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine |
| MFCD00132942 |
| 9H-Purin-6-amine, 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoro- |
| Fludarabine des-phosphate |
| 9-(β-D-Arabinofuranosyl)-2-fluoro-9H-purin-6-amine |
| 9-b-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine |
| (2R,3S,4S,5R)-2-(6-Amino-2-fluoro-9H-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol |
| Fludarabine |
| EINECS 244-525-5 |
| 2-Fluoro-9-b-D-arabinofuranosyladenine |
| F-Ara-A |
| 2-Fluoroadenine-9-β-D-arabinofuranoside |
| 2-F-araA |
| Adenine, 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoro- |
| 2-Fluorovidarabine |

