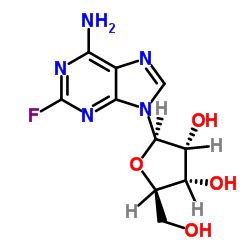
Fludarabine phosphate
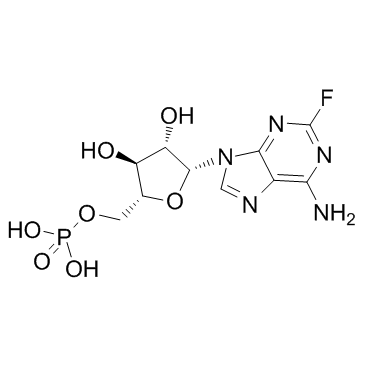
Fludarabine phosphate structure
|
Common Name | Fludarabine phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75607-67-9 | Molecular Weight | 365.212 | |
| Density | 2.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 864.2±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13FN5O7P | Melting Point | 203 °C(dec.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 476.4±37.1 °C | |
Use of Fludarabine phosphateFludarabine (phosphate) is an analogue of adenosine and deoxyadenosine, which is able to compete with dATP for incorporation into DNA and inhibit DNA synthesis. |
| Name | fludarabine phosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fludarabine (phosphate) is an analogue of adenosine and deoxyadenosine, which is able to compete with dATP for incorporation into DNA and inhibit DNA synthesis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Fludarabine phosphate significantly reduces the cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. Fludarabine phosphate exhibits no effect in all tested concentrations when combined with either PBS or control vector, ACE-GFP. Fludarabine phosphate causes a significant decrease in cell viability for 24 h after exposure to ACE-PNP when compared to PBS and ACE-GFP at concentrations of 2.5, 5 and 10 μg/mL[2]. |
| In Vivo | F-araAMP (100 mg/kg given 15 times, 167 mg/kg given 9 times, or 250 mg/kg given 3 times, i.p.) leads to complete regressions of all tumors and cures of all mice. Parental D54 tumors (i.e. without E. coli PNP) are not sensitive to treatment with F-araAMP. Intratumoral injection of Ad/PNP followed by IT F-araAMP can elicit a substantial regressive effect on otherwise refractory solid tumors in a fashion substantially superior to viral PNP transduction followed by systemic prodrug administration[1]. The comparison of ACE-GFP/fludarabine phosphate with ACE-GFP/PBS demonstrats that fludarabine phosphate alone has no growth inhibitory activity on KU-19-19 tumors[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Briefly, 2×103 KU-19-19 cells are seeded in each well of 96-well plates and allowed to grow overnight. Cells are then exposed to PBS, ACE-GFP or ACE-PNP for 3 h. Twenty-four hours post-infection, the cells are treated with various concentrations of fludarabine phosphate. After the 24-h incubation, cytotoxicity is determined by using WST-1; 4-[3-(4-iodophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2H-5-tetrazolio]-1,3-benzene disulfonate. The absorbance value is determined at 450 nm by a microplate reader. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Parental and E. coli PNP expressing D54MG (human glioma) tumor cells (2×107 cells) are injected subcutaneously into the flanks of nude mice (nu/nu). D54 tumor cells stably transduced with E. coli PNP are prepared as described previously. Tumors are measured with calipers and an estimate of the weight calculated using the equation, (length × width2)/2=mm3, and converted to mg assuming unit density. Unless stated otherwise, therapeutic drugs and the adenoviral vector expressing E. coli PNP (Ad/PNP), or vehicle controls are injected into D54 tumors in 150 μL volumes by 8 separate injections of approximately 20 μL each in an effort to evenly distribute the administered agent. At least 6 mice are studied in each treatment group. Mice are monitored daily and body weights and tumor dimensions collected twice weekly. T-C (tumor growth delay) is determined as the difference in median days to 2 doublings (median days to 600 mg for the D54 and DU145 (human prostate cancer) analysis) between drug-treated and vehicle-treated groups. For the NIH-H322M (human non-small cell lung cancer) study, because of tumor proliferation characteristics, total growth inhibition (TGI) is used as the evaluation point. TGI is equal to the control group mean delta minus the treated group mean delta divided by the control group mean delta, where delta is the change in tumor weight for each animal between day 36 and day 59. The time to the evaluation point for each animal is used as the end point for the student's t-test, Mann-Whitney rank sum test, or a life table analysis in order to statistically compare growth data between treatment groups. All key results are repeated under similar conditions and findings confirmed. Treatments are initiated when tumors are 250 to 300 mg (appr 1-1.5% of total animal weight). |
| References |
| Density | 2.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 864.2±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 203 °C(dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13FN5O7P |
| Molecular Weight | 365.212 |
| Flash Point | 476.4±37.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 365.053650 |
| PSA | 195.88000 |
| LogP | 0.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.879 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | T |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R25:Toxic if swallowed. |
| Safety Phrases | S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|
~41% 
Fludarabine pho... CAS#:75607-67-9 |
| Literature: ADORKEM TECHNOLOGY SPA Patent: WO2005/40183 A2, 2005 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 4-5 ; |
|
~% 
Fludarabine pho... CAS#:75607-67-9 |
| Literature: US5296589 A1, ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Population pharmacokinetic/dynamic model of lymphosuppression after fludarabine administration.
Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 75(1) , 67-75, (2015) Quantitative relationships between 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine (F-ara-A) concentrations and lymphosuppression have not been reported, but would be useful for regimen design. A population ph... |
|
|
Fludarabine phosphate in lymphoma: an important new therapeutic agent.
Cancer Treat. Res. 85 , 3-14, (1996)
|
|
|
Fludarabine phosphate in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: biology, clinical impact, and future directions.
Cancer Treat. Res. 64 , 105-19, (1993)
|
| 2-Fluoro-9-(5-O-phosphono-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-9H-purin-6-amine |
| 2-fluoro-araamp |
| Fludara |
| Fludarabin Phosphate |
| Fludarabine (phosphate) |
| 2-fluoro-ara-C-5'-O-phosphate |
| 2-Fluoroadenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate |
| fludarabinemonophosphate |
| Fludarabine 5'-Phosphate |
| fludarabine hcl |
| fludarabine monophosphate |
| Fludura |
| Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara) |
| Fludarabine 5'-monophosphate |
| Fludarabine phosphate |
| fludarabine |
| 9H-Purin-6-amine, 2-fluoro-9-(5-O-phosphono-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)- |
| FLUDARUBINE PHOSPHATE |
| [(2R,3S,4S,5R)-5-(6-amino-2-fluoro-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate |
| F-ara-AMP |
| FAMP |
| MFCD00866418 |