N-Vinylcaprolactam
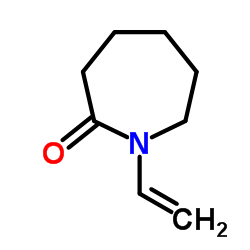
N-Vinylcaprolactam structure
|
Common Name | N-Vinylcaprolactam | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2235-00-9 | Molecular Weight | 139.195 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 254.7±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H13NO | Melting Point | 35-38 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 112.5±9.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | N-Vinylcaprolactam |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 254.7±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 35-38 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H13NO |
| Molecular Weight | 139.195 |
| Flash Point | 112.5±9.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 139.099716 |
| PSA | 20.31000 |
| LogP | 1.50 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.548 |
| InChIKey | JWYVGKFDLWWQJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C=CN1CCCCCC1=O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312-H317-H319-H372 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P280-P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Target Organs | Liver, Upper respiratory tract |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R41 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933790090 |
|
~% 
N-Vinylcaprolactam CAS#:2235-00-9 |
| Literature: US2806847 , ; US2806848 , ; |
|
~81% 
N-Vinylcaprolactam CAS#:2235-00-9 |
| Literature: Boettcher, Arnd; Pinkos, Rolf; Preiss, Thomas; Lorenz, Rudolf Erich Patent: US2003/28035 A1, 2003 ; |
|
~% 
N-Vinylcaprolactam CAS#:2235-00-9 |
| Literature: Gazzetta Chimica Italiana, , vol. 123, # 8 p. 457 - 462 |
|
~% 
N-Vinylcaprolactam CAS#:2235-00-9 |
| Literature: Gazzetta Chimica Italiana, , vol. 123, # 8 p. 457 - 462 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 2933790090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933790090. other lactams. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:9.0%. . MFN tariff:9.0%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Toward the dynamic phase transition mechanism of a thermoresponsive ionic liquid in the presence of different thermoresponsive polymers.
Soft Matter 12 , 925-33, (2016) The influence of two thermoresponsive polymers, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) and poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) (PVCL), on the phase transition behavior of a thermoresponsive ionic liquid, tributylh... |
|
|
Facile fabrication of P(OVNG-co-NVCL) thermoresponsive double-hydrophilic glycopolymer nanofibers for sustained drug release.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 135 , 209-16, (2015) The thermoresponsive double-hydrophilic glycopolymer (DHG), Poly (6-O-vinyl-nonanedioyl-D-galactose-co-N-vinylcaprolactam) (P(OVNG-co-NVCL)) was synthesized via a chemo-enzymatic process and a free ra... |
| 1-Vinylazepan-2-one |
| N-VinylcaprolaCLaM |
| N-VINYL-E-CAPROLACTAM |
| n-vinyl caprolactam |
| N-Vinyl-ε-caprolactam |
| n-vinyl |
| UNII-KFC10CY9UP |
| 2H-Azepin-2-one, 1-ethenylhexahydro- |
| 1-Vinyl-2-azepanone |
| 1-vinyl-perhydro-azepin-2-one |
| EINECS 218-787-6 |
| VCAP |
| N-Vinyl-epsilon-caprolactam |
| 1-Ethenylhexahydro-2H-azepin-2-one |
| NVCL |
| MFCD00080693 |
| vinyl caprolactam |
| 1-ethenylazepan-2-one |
| N-Vinyl-2-Caprolactam |

 CAS#:19797-08-1
CAS#:19797-08-1 CAS#:1020572-61-5
CAS#:1020572-61-5 CAS#:3420-84-6
CAS#:3420-84-6 CAS#:1487-12-3
CAS#:1487-12-3 CAS#:860190-32-5
CAS#:860190-32-5
