Fosfomycin
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 08:30:34
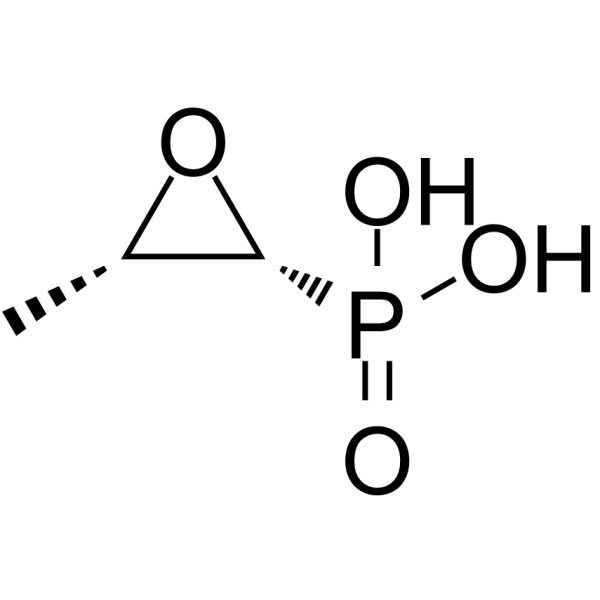
Fosfomycin structure
|
Common Name | Fosfomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23155-02-4 | Molecular Weight | 138.05900 | |
| Density | 1.561g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 342.651ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7O4P | Melting Point | 94ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 161.03ºC | |
Use of FosfomycinFosfomycin (MK-0955) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Fosfomycin can cross blood-brain barrier penetrating, and irreversibly inhibits an early stage in cell wall synthesis. Fosfomycin shows anti-bacteria activity for a range of bacteria, including multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and pan-drug-resistant (PDR) bacteria[1][2]. |
| Name | fosfomycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fosfomycin (MK-0955) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Fosfomycin can cross blood-brain barrier penetrating, and irreversibly inhibits an early stage in cell wall synthesis. Fosfomycin shows anti-bacteria activity for a range of bacteria, including multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and pan-drug-resistant (PDR) bacteria[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Fosfomycin (80 mg/kg; i.v. or p.o.) displays the protective effect on the nephrotoxicity of double beckacin, and is not affected by different administration routes in rats[3]. Pharmacokinetic of Fosfomycin in Rats[4] Dibekacin Dose (mg) Vdss (l/kg) β (min-1) T1/2 (min) Urinary recovery (%) 30 0.261 0.0244 28.4 85 Animal Model: Fischer 344 rats[3] Dosage: 320 mg/kg Administration: Intramuscular injection, 5 schedules: 1 h, 0.5 h earlier than dibekacin, concomitantly, 0.5 h later and 1 h later; 11 days Result: Reduced polyuria, proteinuria, enzymes and cytosine caused by dibecacin (40 mg/kg), followed by the previous treatment. Animal Model: Dehydrated Wistar rat with acute renal failure (8-week-old)[4] Dosage: 120 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection; once Result: Recovered the exclusion rate of rats basically to normal, and improved the nephrotoxicity parameters. Protects proximal tubular lysosomes from aminoglycosides by inhibiting myeloid formation and protecting the integrity of lysosomal membrane of rats treated with double bekacin. |
| References |
[1]. Falagas ME, et al. Fosfomycin. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Apr. 29(2):321-47. |
| Density | 1.561g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 342.651ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 94ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7O4P |
| Molecular Weight | 138.05900 |
| Flash Point | 161.03ºC |
| Exact Mass | 138.00800 |
| PSA | 79.87000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.486 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| HS Code | 2931900090 |
|---|
| HS Code | 2931900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2931900090. other organo-inorganic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward). MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
| Veramina |
| MFCD00242804 |
| Fosfocina |
| [(2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-yl]phosphonic acid |
| phosphomycin |
| Fosfomycinum |
| FOSFOMYCIN |
| Fosfomicina |
| EINECS 245-463-1 |
| Phosphonomycin |
| Fosfomycine |
 CAS#:26016-99-9
CAS#:26016-99-9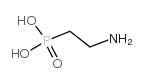 CAS#:2041-14-7
CAS#:2041-14-7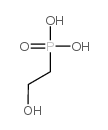 CAS#:22987-21-9
CAS#:22987-21-9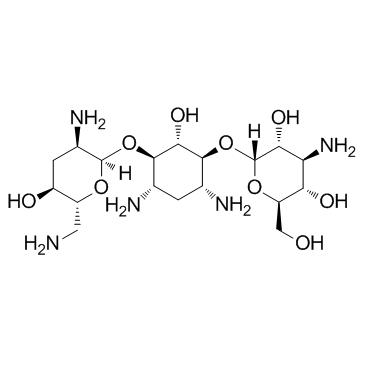 CAS#:32986-56-4
CAS#:32986-56-4