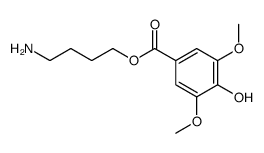
Leonurine

Leonurine structure
|
Common Name | Leonurine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 24697-74-3 | Molecular Weight | 311.334 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 496.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H21N3O5 | Melting Point | 191-193ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 254.2±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of LeonurineLeonurine is an alkaloid isolated from Herba leonuri, with anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory. |
| Name | 4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Leonurine is an alkaloid isolated from Herba leonuri, with anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Leonurine (0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 µM) causes diminution in lipid accumulation, cellular cholesterol content, including total cholesterol (TC), free cholesterol (FC) and cholesteryl ester (CE), and increase in apoA-I- or HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux after treatment for 24 h. Leonurine also significantly and dose-dependently increases the expressions of ABCA1 and ABCG1 at the mRNA and protein levels in human THP-1 macrophages, and such effect is involved in PPARγ[1]. Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) shows protective effect on cell viability of HepG2 and HL-7702 cells incubated with palmitic acid (PA) of free fatty acid (FFA) for 24 h. Leonurine hydrochloride (125, 250, 500 μM) improves cellular lipid accumulation in HepG2 and HL-7702 cells via activating AMPK/SREBP1 pathway[2]. Leonurine (5, 10, 20 µM) inhibits the expression of iNOS, COX-2, PGE2, NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 in IL-1β-induced human chondrocytes, suppresses ECM degradation in human OA chondrocytes, and blocks IL-1β-induced PI3K and Akt phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner[3]. |
| In Vivo | Leonurine (10 mg/kg/d, p.o.) significantly increases the expressions of PPARγ, LXRα, ABCA1 and ABCG1, and decreases both TG and TC levels in serum of mice[1]. Leonurine hydrochloride (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) improves intracellular lipid accumulation via activating AMPK/SREBP1 pathway, enhances biochemical parameters, reduces hepatic lipoperoxide and increases antioxidant levels in mice[2]. Leonurine (20 mg/kg, p.o.) ameliorates osteoarthritis development in mouse DMM model[3]. |
| Cell Assay | MTT assay is performed to study the cytotoxic effects of Leonurinein HepG2 and HL-7702 cells. Briefly, HepG2 and HL-7702 cells are seeded for 24 h at the density of 3 × 104 cells/well in 96-well plates. After 24 h incubation, cells are treated with different concentrations of Leonurine (0-1000 μM) and the control group is treated with only DMEM for 24 h at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator. Then, these cells are treated with MTT solution (5 mg/mL) for further 4 h. After 4 h incubation, DMEM containing MTT solution is discarded. Cells are then dissolved by adding DMSO (200 μL) to each well and the solutions are mixed thoroughly for 5 min. Finally, the absorbance is determined at 570 nm with a microplate reader[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] ApoE-/- mice (male, eight-week old) are fed a chow diet for 2 weeks, apoE-/- mice are randomly divided into several groups (n=15/group). Mice in the Leonurine group are intragastrically administered with Leonurine (10 mg/kg/d) every day and continued for 8 weeks. The control group is fed with an equal volume of PBS. At week 16, mice are euthanized, followed by collecting the blood and tissue samples for further analyses[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 496.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 191-193ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C14H21N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 311.334 |
| Flash Point | 254.2±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 311.148132 |
| PSA | 126.89000 |
| LogP | 0.22 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.554 |
| InChIKey | WNGSUWLDMZFYNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(C(=O)OCCCCN=C(N)N)cc(OC)c1O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble2mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|
~29% 
Leonurine CAS#:24697-74-3 |
| Literature: European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 46, # 9 p. 3996 - 4009 |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Leonurus japonicus, Leonurus cardiaca, Leonotis leonurus: a novel HPLC study on the occurrence and content of the pharmacologically active guanidino derivative leonurine.
Pharmazie 67(12) , 973-9, (2012) Leonurine is a prominent pharmacologically active guanidine alkaloid (4-{[amino(imino)methyl]amino} butyl-4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate), mainly exerting cardiovascular, hypotensive, uterotonic, and... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of stachydrine and leonurine in rat plasma after oral administration of Herba Leonuri extract by LC-MS/MS.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 76 , 192-9, (2013) A simple, sensitive and specific method was developed for simultaneous determination of stachydrine and leonurine in rat plasma using diphenhydramine as an internal standard (IS). The separation was p... |
|
|
Quantification of leonurine, a novel potential cardiovascular agent, in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to pharmacokinetic study in rats.
Biomed. Chromatogr. 26(4) , 518-23, (2012) Leonurine (SCM-198), an alkaloid from Herba Leonuri, has been suggested as a novel cardiovascular agent by pharmacology studies in preclinical stage. In present study, we report a simple, rapid and se... |
| Leonurine hydrochloride |
| Leonurine |
| 4-Guanidinobutyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate |
| 4-Guanidino-1-butanol syringate 4-Guanidinobutyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate SCM-198 |
| 4-Guanidino-n-butyl syringate |