Asperglaucin B
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 20:31:47
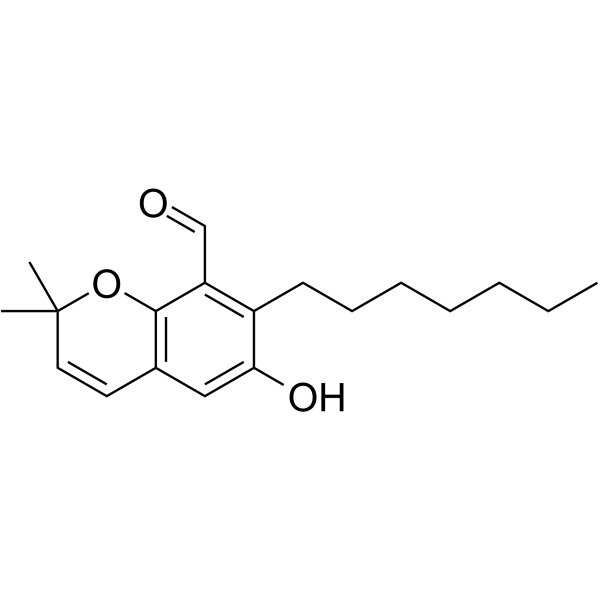
Asperglaucin B structure
|
Common Name | Asperglaucin B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2701570-80-9 | Molecular Weight | 302.41 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H26O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Asperglaucin BAsperglaucin B is an alkylated salicylaldehyde derivative from the fungus Aspergillus chevalieri SQ-8, with antibacterial activities. Asperglaucin B displays potent antibacterial activities against two plant pathogens Pseudomonas syringae pv actinidae (Psa) and Bacillus cereus, with an MIC value of 6.25 μM[1]. |
| Name | Asperglaucin B |
|---|
| Description | Asperglaucin B is an alkylated salicylaldehyde derivative from the fungus Aspergillus chevalieri SQ-8, with antibacterial activities. Asperglaucin B displays potent antibacterial activities against two plant pathogens Pseudomonas syringae pv actinidae (Psa) and Bacillus cereus, with an MIC value of 6.25 μM[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MIC: 6.25 μM (Pseudomonas syringae pv actinidae (Psa) and Bacillus cereus)[1] |
| In Vitro | The possible bacteriostatic mechanism for Asperglaucin B is to alter the external structure of B. cereus and Psa, and to cause the rupture or deformation of the cell membranes, respectively[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C19H26O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 302.41 |
| InChIKey | LXXMLVSDFZLIEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCc1c(O)cc2c(c1C=O)OC(C)(C)C=C2 |