Etoposide
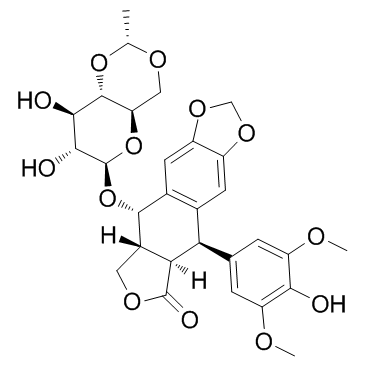
Etoposide structure
|
Common Name | Etoposide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 33419-42-0 | Molecular Weight | 588.557 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 798.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H32O13 | Melting Point | 236-251ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 263.6±26.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of EtoposideEtoposide is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer. Etoposide inhibits DNA synthesis by forming a complex with topoisomerase II and DNA. |
| Name | etoposide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Etoposide is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer. Etoposide inhibits DNA synthesis by forming a complex with topoisomerase II and DNA. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase II |
| In Vitro | Etoposide is capable of causing cytotoxicity on pancreatic β-cells by inducing apoptosis through the JNK/ERK-mediated GSK-3 downstream-triggered mitochondria-dependent signaling pathway in RIN-m5F cells[1]. Etoposide and Bevacizumab significantly abolish P1 sphere-forming ability, an effect associated with apoptosis of this subset of cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Etoposide (50 μM) and Bevacizumab-treated hypoxic cells injected intravenously into immunodeficient mice reveals a reduced capacity to induce lung colonies, which also appear with a longer latency period[2]. Etoposide (10 mg/kg/day, i.v.) with ifosfamide and carboplatin, reduces the tumor volume in the hepatoblastoma cell injected NMRI nude mice[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | RIN-m5F cells are seeded and treated with Etoposide (10-50 μM) in the absence or presence of Z-DEVD-FMK (20 μM). At the end of treatments (for 24 h), the cell lysates are incubated at 37°C with 10 μM Ac-DEVD-AMC, a caspase-3/CPP32 substrate, for 1 h. The fluorescence of the cleaved substrate is measured by a spectrofluorometer with an excitation wavelength at 380 nm and an emission wavelength at 460 nm. Protein levels of cell lysate samples are determined using the bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit with an absorption band of 570 nm to normalize the cell numbers between control and etoposide-treated groups. |
| Cell Assay | RIN-m5F cell is a rat pancreatic β-cell line, and cultured in a humidified chamber with a 5% CO2-95% air mixture at 37°C and maintained in RPIM 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotics (100 U/mL of penicillin and 100 μg/mL of streptomycin). RIN-m5F cells are seeded (2 × 104 cells/well) in 96-well plates and allowed to adhere and recover overnight. The cells are changed to fresh media and then incubated with Etoposide (1-100 μM) in the absence or presence of the pharmacological inhibitors (lithium chloride (LiCl)-50 μM; SP600125-20 μM; PD98059-20 μM) for 24 h. |
| Animal Admin | The in vivo model for nude mice HB (NMHB) has been established. Only HB cells with embryonal components are grafted and reproduced successfully in this model. Each NMHB subsequently is transplanted into 50 mice for treatment groups. Treatment is initiated when the majority of the tumors reach a volume of 50-100 mm3. The mice are stratified according to their tumor volume and randomLy assigned to groups of ten animals each. The animals injected with tumor are given ifosfamide, cisplatin, doxorubicin, etoposide (10 mg/kg/day, i.v.), and carboplatin as single agents in two blocks. One group of ten animals for each original xenograft served as a control group. After initiation of treatment, the tumor growth is recorded at 5-day intervals for 25-30 days and the relative tumor volumes are calculated. Twenty-four hours before the animals are sacrificed, bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) is injected intraperitoneally for the semiquantitative determination of proliferation activity of the tumor cells (50 μg of BrdU/g body weight). |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 798.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 236-251ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C29H32O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 588.557 |
| Flash Point | 263.6±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 588.184265 |
| PSA | 160.83000 |
| LogP | 0.30 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.662 |
| InChIKey | VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-NBJJDLTASA-N |
| SMILES | COc1cc(C2c3cc4c(cc3C(OC3OC5COC(C)OC5C(O)C3O)C3COC(=O)C23)OCO4)cc(OC)c1O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P280-P301 + P312 + P330-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic |
| Risk Phrases | R45;R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | KC0190000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
TAp73 promotes cell survival upon genotoxic stress by inhibiting p53 activity.
Oncotarget 5(18) , 8107-22, (2014) p53 plays a key role in regulating DNA damage response by suppressing cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis depending on extent of DNA damage. However, it is not clear why mild genotoxic stress... |
|
|
DNA damage-specific deubiquitination regulates Rad18 functions to suppress mutagenesis.
J. Cell Biol. 206(2) , 183-97, (2014) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) lesions encountered during replication are often bypassed using DNA damage tolerance (DDT) pathways to avoid prolonged fork stalling and allow for completion of DNA replica... |
|
|
SK053 triggers tumor cells apoptosis by oxidative stress-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 93(4) , 418-27, (2015) Thioredoxins (Trx) together with thioredoxin reductases (TrxR) participate in the maintenance of protein thiol homeostasis and play cytoprotective roles in tumor cells. Therefore, thioredoxin-thioredo... |
| (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-9-{[(2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-methylhexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]oxy}-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6(5aH)-one |
| VP-16-213 |
| 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-ethylidene-β-D-glucopyranoside) |
| Vepeside |
| Etoposide |
| 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin ethylidene-β-D-glucoside |
| EPEG |
| MFCD00869325 |
| Etoposide [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN] |
| Etoposide USP26 |
| Etoposide (VP16) |
| (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-9-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-8-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-9-{[(2R,4aR,6R,7R,8R,8aS)-7,8-dihydroxy-2-méthylhexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl]oxy}-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diméthoxyphényl)-5,8,8a,9-tétrahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphto[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6(5aH)-one |
| 4′-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-ethylidene-β-D-glucopyranoside) |
| Furo[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d]-1,3-dioxol-6(5aH)-one, 9-[[4,6-O-[(1R)-ethylidene]-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5,8,8a,9-tetrahydro-5-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-, (5R,5aR,8aR,9S)- |
| 4‘-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-ethylidene-β-D-glucopyranoside) |
| EINECS 251-509-1 |
![benzyl (4-((5R,5aR,8aR,9S)-9-(((2R,4aR,6R,7R,8S,8aR)-7,8-bis(benzyloxy)-2-methylhexahydropyrano[3,2-d][1,3]dioxin-6-yl)oxy)-6-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl) carbonate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/070/270928-23-9.png) CAS#:270928-23-9
CAS#:270928-23-9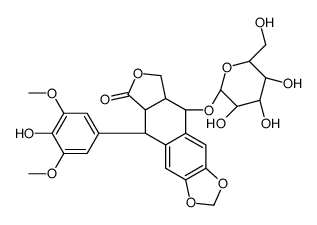 CAS#:23363-35-1
CAS#:23363-35-1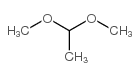 CAS#:534-15-6
CAS#:534-15-6 CAS#:6559-91-7
CAS#:6559-91-7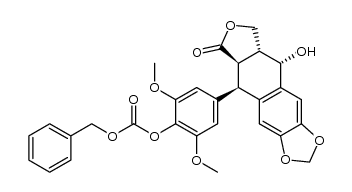 CAS#:23363-33-9
CAS#:23363-33-9 CAS#:23363-34-0
CAS#:23363-34-0 CAS#:3947-62-4
CAS#:3947-62-4 CAS#:138261-30-0
CAS#:138261-30-0
