Sphingomyelins (egg)
Modify Date: 2024-01-09 18:41:50
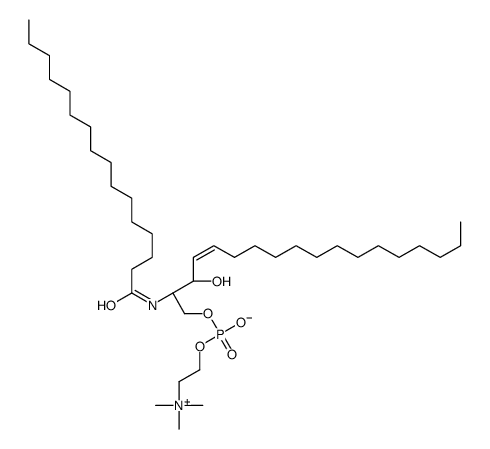
Sphingomyelins (egg) structure
|
Common Name | Sphingomyelins (egg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 383907-87-7 | Molecular Weight | 703.02800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C39H79N2O6P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Sphingomyelins (egg)As a major constituent of cell membranes, sphingomyelin is found at particularly high concentrations in the membranes of nerve cells (in the myelin sheaths) and red blood cells. It was previously thought to have a purely structural role, similar to the function of phosphatidylcholine, through intermolecular interactions mediated by the 2-amide group, the 3-hydroxy group and the 4,5-trans double bond of the sphingoid base. However, it is now appreciated that sphingomyelin has a high affinity for cholesterol and that these two lipids pack tightly into liquid-ordered domains among a liquid-disordered phase to form lipid rafts. |
| Name | (2S,3S,4E)-3-Hydroxy-2-(palmitoylamino)-4-octadecen-1-yl 2-(trime thylammonio)ethyl phosphate |
|---|
| Molecular Formula | C39H79N2O6P |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 703.02800 |
| Exact Mass | 702.56800 |
| PSA | 121.22000 |
| LogP | 11.68900 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
|---|