Dihydrocytochalasin B
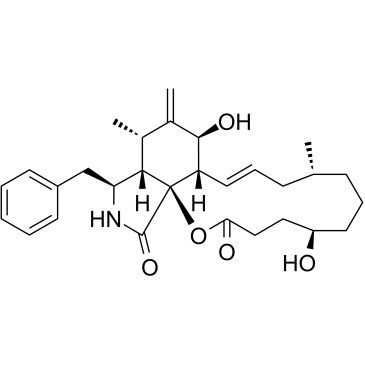
Dihydrocytochalasin B structure
|
Common Name | Dihydrocytochalasin B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39156-67-7 | Molecular Weight | 481.62400 | |
| Density | 1.194g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 727.474ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39NO5 | Melting Point | 203-205ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 393.762ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Dihydrocytochalasin BDihydrocytochalasin B is a Cytokinesis inhibitor and changes the morphology of the cells, similar to that of cytochalasin B; does not inhibit glucose transport[1]. Dihydrocytochalasin B (H2CB) disrupts the actin structure and inhibits the ability of growth factors to stimulate DNA synthesis, reversibly blocks initiation of DNA synthesis, causes cell rounding and a loss of actin microfilament bundles[2]. Dihydrocytochalasin B is related to transcytoplasmic movement of calcium by inhibiting active calcium transport and causes a Ca+increase in the mucosal scrapings[3]. |
| Name | dihydrocytochalasin b |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dihydrocytochalasin B is a Cytokinesis inhibitor and changes the morphology of the cells, similar to that of cytochalasin B; does not inhibit glucose transport[1]. Dihydrocytochalasin B (H2CB) disrupts the actin structure and inhibits the ability of growth factors to stimulate DNA synthesis, reversibly blocks initiation of DNA synthesis, causes cell rounding and a loss of actin microfilament bundles[2]. Dihydrocytochalasin B is related to transcytoplasmic movement of calcium by inhibiting active calcium transport and causes a Ca+increase in the mucosal scrapings[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.194g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 727.474ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 203-205ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 481.62400 |
| Flash Point | 393.762ºC |
| Exact Mass | 481.28300 |
| PSA | 95.86000 |
| LogP | 4.04490 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.584 |
| InChIKey | WIULKAASLBZREV-CJKMDAKDSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C1C(C)C2C(Cc3ccccc3)NC(=O)C23OC(=O)CCC(O)CCCC(C)CC=CC3C1O |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300-H310-H330-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P284-P302 + P350-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+,T |
| Risk Phrases | 26/27/28-40 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
Tetraploidization increases sensitivity to Aurora B kinase inhibition.
Cell Cycle 11(13) , 2567-77, (2012) Aurora kinases are overexpressed in many cancers and are targets for anticancer drugs. The yeast homolog of Aurora B kinase, IPL1, was found to be a ploidy-specific lethality gene. Given that polyploi... |
|
|
Centrifugal and chromatographic analyses of tryptophan and tyrosine uptake by red blood cells and GLUT1 proteoliposomes with permeability estimates and observations on dihydrocytochalasin B.
J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 55(2) , 127-40, (2003) We analyzed transport into liposomes and proteoliposomes, separated the free and internalized radioactively labeled substrates by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and observed a net influx owing to... |
|
|
Degradation and recycling of the substrate-binding subunit of type II iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase in astrocytes.
J. Biol. Chem. 271(27) , 16369-74, (1996) Thyroxine dynamically regulates levels of type II iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase (5'D-II) by modulating enzyme inactivation and targeting the enzyme to different pathways of internalization. 5'D-II is an... |
| 2,3-Dihydro-cytochalasin B |
| 21,22-dihydro-phomin |
| EINECS 254-324-4 |
| 21,22-Dihydrocytochalalsin B |
| CYTOCHALASIN B,DIHYDRO |
| 21,22-dihydro-cytochalasin-B |
| dihydrocytocholasin-B |
| 7(S),20(R)-dihydroxy-16(R)-methyl-10-phenyl-24-oxa[14]cytochalasa-6(12),13(E)-diene-1,23-dione |
| DHCB |
| (7S,13E,16R,20R)-7,20-Dihydroxy-16-methyl-10-phenyl-24-oxa[14]cytochalasa-6(12),13-diene-1,23-dione |
| MFCD00010541 |