Kamebanin
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 10:24:51
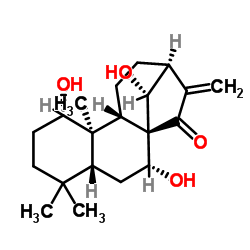
Kamebanin structure
|
Common Name | Kamebanin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39388-57-3 | Molecular Weight | 334.45 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 514.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 278.8±26.6 °C | |
Use of KamebaninKamebanin can be isolated from the leaves of Isodon weisiensis C. Y. Wu. Kamebanin has anti-proliferative activity and can be used in cancer research[1]. |
| Name | (1α,5β,7α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14R)-1,7,14-Trihydroxykaur-16-en-15-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Kamebanin can be isolated from the leaves of Isodon weisiensis C. Y. Wu. Kamebanin has anti-proliferative activity and can be used in cancer research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 514.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 334.45 |
| Flash Point | 278.8±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 334.214417 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 1.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.582 |
| InChIKey | VSDVMWBRICFVRW-BIGDWJEQSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C1C(=O)C23C(O)CC4C(C)(C)CCC(O)C4(C)C2CCC1C3O |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| (1α,5β,7α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14R)-1,7,14-Trihydroxykaur-16-en-15-one |

