Ferutinin
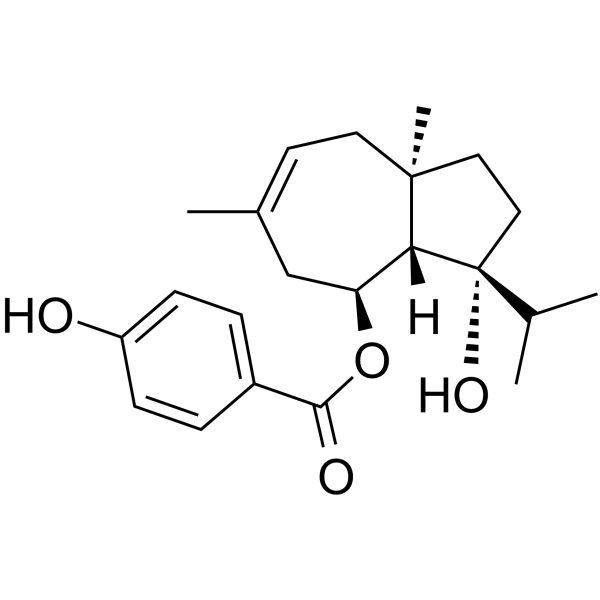
Ferutinin structure
|
Common Name | Ferutinin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 41743-44-6 | Molecular Weight | 358.47 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 489.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H30O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 164.4±22.2 °C | |
Use of FerutininFerutinin, a natural terpenoid compound, is an estrogen receptor ERα agonist and estrogen ERβ-receptor agonist/antagonist with IC50s of 33.1 nM and 180.5 nM, respectively. Ferutinin acts as an electrogenic Ca2+-ionophore that increases calcium permeability of lipid bilayer membranes, mitochondria. Ferutinin possesses estrogenic, antitumor, antibacterial and antiinflammatory activities[1][2]. |
| Name | ferutinin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ferutinin, a natural terpenoid compound, is an estrogen receptor ERα agonist and estrogen ERβ-receptor agonist/antagonist with IC50s of 33.1 nM and 180.5 nM, respectively. Ferutinin acts as an electrogenic Ca2+-ionophore that increases calcium permeability of lipid bilayer membranes, mitochondria. Ferutinin possesses estrogenic, antitumor, antibacterial and antiinflammatory activities[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ERα:33.1 nM (IC50) ERβ:180.5 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Ferutinin manifested antiproliferative activity, inducing apoptosis in several cell types: MCF-7 estrogen-dependent cancer cells, leukemia T-cell line (Jurkat), human and mouse colon carcinoma cells (Caco-2, CT26, HT29), as well as bladder (TCC) cancer cells. Ferutinin potentiates bone mineralization, and is proposed to be used as an antiosteoporosis phytoestrogen[2]. Ferutinin considerably increases the permeability of artificial and cellular membranes to Ca2+-ions and produces apoptotic cell death in different cell lines in a mitochondria-dependent manner. Ferutinin alone (10-60 µM) also dose-dependently dissipated membrane potential. In the presence of Ca2+-ions, Ferutinin (10-60 µM) induces considerable depolarization of the inner mitochondrial membrane[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 489.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C22H30O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 358.47 |
| Flash Point | 164.4±22.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 358.214417 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 5.72 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.573 |
|
~% 
Ferutinin CAS#:41743-44-6 |
| Literature: Tolstikov, G. A.; Akbutina, F. A.; Dembitskii, A. D.; Valeev, F. A.; Miftakhov, M. S. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1992 , vol. 28, # 10 p. 1666 - 1673 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1992 , vol. 28, # 10 p. 2081 - 2090 |
|
~% 
Ferutinin CAS#:41743-44-6 |
| Literature: Tolstikov, G. A.; Akbutina, F. A.; Dembitskii, A. D.; Valeev, F. A.; Miftakhov, M. S. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1992 , vol. 28, # 10 p. 1666 - 1673 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1992 , vol. 28, # 10 p. 2081 - 2090 |
|
~% 
Ferutinin CAS#:41743-44-6 |
| Literature: Tolstikov, G. A.; Akbutina, F. A.; Dembitskii, A. D.; Valeev, F. A.; Miftakhov, M. S. Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1992 , vol. 28, # 10 p. 1666 - 1673 Zhurnal Organicheskoi Khimii, 1992 , vol. 28, # 10 p. 2081 - 2090 |
| jaeschkeanadiol p-hydroxybenzoate |
| L57 GUTJ BY1&1 BQ E1 H1 JOVR DQ &&Stereoisomer |
| jaeschkeanadiol o-hydroxybenzoate |
| Benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-, (3R,3aS,4S,8aR)-1,2,3,3a,4,5,8,8a-octahydro-3-hydroxy-6,8a-dimethyl-3-(1-methylethyl)-4-azulenyl ester |
| ferutinol p-hydroxybenzoate |
| (3R,3aS,4S,8aR)-3-Hydroxy-3-isopropyl-6,8a-dimethyl-1,2,3,3a,4,5,8,8a-octahydro-4-azulenyl 4-hydroxybenzoate |
| Hecameg |

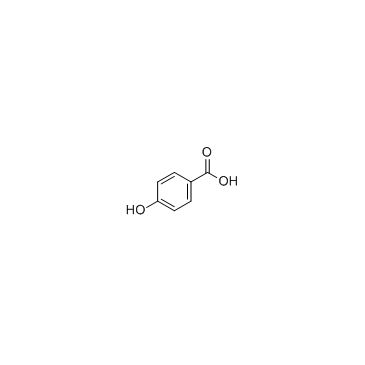 CAS#:99-96-7
CAS#:99-96-7