LCS-1
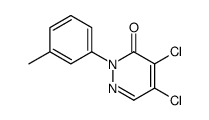
LCS-1 structure
|
Common Name | LCS-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 41931-13-9 | Molecular Weight | 255.10000 | |
| Density | 1.39g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 339.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8Cl2N2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 159.2ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of LCS-1LCS-1 is a superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) inhibitor. LCS-1 inhibits SOD1 activity with an IC50 value of 1.07 μM. LCS-1 induces the early- and late-stage apoptosis of multiple myeloma (MM.1S) cells[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 4,5-dichloro-2-(3-methylphenyl)pyridazin-3-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | LCS-1 is a superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) inhibitor. LCS-1 inhibits SOD1 activity with an IC50 value of 1.07 μM. LCS-1 induces the early- and late-stage apoptosis of multiple myeloma (MM.1S) cells[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
SOD1:1.07 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | LCS-1 (1-10000 nM; 24 hours) has selective cytotoxicity towards bloom syndrome gene product (BLM) -proficient and BLM-deficient HCT116 cells[1]. LCS-1 shows growth inhibitory effect on 10/27 adenocarcinoma cell lines (median IC50=0.20 μM; such as H23, H2347, HCC827 cell lines) and normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells (IC50=2.66 μM)[2]. LCS-1 (0, 1.25, 2 μM; 4 h) in a concentration-dependent manner triggers significant inhibition of SOD1 enzymatic activity in multiple myeloma (MM) cells[3]. LCS-1 (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5 μM; 48 h) in a dose-dependent manner reduces the viability of various MM cell lines, including MM.1R (Dexamethasone-resistant), Dox40 (Doxorubicin-resistant), or LR5 (Melphalan-resistant) cell lines[3]. LCS-1 (48 h) has IC50 values of 2.5 and 4.6 μM for cell viability of ANBL6-WT (Bortezomib-sensitive) and ANBL6-BR (Bortezomib- resistant) cells, respectively[3]. LCS-1 (1.25 μM; 16 h) induces a significant increase in ROS levels and O2− levels in MM.1S cells[3]. LCS-1 (1.25 μM; 16 h) shows a significant decrease in GSH/GSSG ratio in MM.1S cells[3]. LCS-1 (1.25 μM; 24h) induces the release of mitochondrial cytochrome-c into the cytosol, and enriches the proteins (HSP60/CLPP) mediating mtUPR signaling in MM.1S cells[3]. LCS-1-induced O2− (1.25 μM; 5 h) triggers a marked decrease in both RP2CP and RP1CP forms of 26S proteasomes[3]. LCS-1 (2 μM; 16 h) induces the early- and late-stage apoptosis of MM.1S cells[3]. LCS-1 (0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 μM) upregulates p53/p21 signaling, as well as downregulates survival pathway proteins MCL-1, BclxL, or c-Myc in MM.1S cells[3]. LCS-1 (0, 4, 8, 16, 24 h; 2 μM) shows a rapid and robust induction of mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPR) proteins (BIP, PERK, phosphorylated eIF2α, or a lectin protein calnexin) in MM.1S and ANBL6-BR cells[3]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: BLM-proficient and BLM-deficient HCT116 cells Concentration: 1-10000 nM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Had IC50 values of 1462 nM and 24.92 nM for the viability of BLM-proficient and BLM-deficient HCT116 cells, respectively. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: MM.1S and ANBL6-BR cells Concentration: 2 μM Incubation Time: 16 hours Result: Decreased the expression of cell-cycle regulatory proteins (cyclin-B1, CDC25C, and CDC2). Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: MM.1S cells Concentration: 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 μM Incubation Time: Result: Upregulated p53/p21 signaling, as well as downregulated survival pathway proteins MCL-1, BclxL, or c-Myc. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: MM.1S cells Concentration: 2 μM Incubation Time: 0, 4, 8, 16, 24 hours Result: Showed a rapid and robust induction of UPR proteins (BIP, PERK, phosphorylated eIF2α, or a lectin protein calnexin). |
| In Vivo | LCS-1 (20 mg/kg; i.p. every other day for 14 days) inhibits MM growth and prolongs host survival in MM.1S-bearing mice[3]. Animal Model: 5-week-old female CB17 SCID mice (MM.1S tumors volume=100 mm3)[3] Dosage: 20 mg/kg (diluted in saline) Administration: Intraperitoneal injections; treated on an every other day schedule for 14 days Result: Inhibited MM growth and prolongs host survival. |
| References |
| Density | 1.39g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 339.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8Cl2N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 255.10000 |
| Flash Point | 159.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 254.00100 |
| PSA | 34.89000 |
| LogP | 2.84770 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to beige |
| Index of Refraction | 1.627 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble10mg/mL (clear solutikon, warmed) |
|
~10% 
LCS-1 CAS#:41931-13-9 |
| Literature: MEMORIAL SLOAN-KETTERING CANCER CENTER Patent: WO2008/80056 A2, 2008 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 94 ; |
|
~% 
LCS-1 CAS#:41931-13-9 |
| Literature: Urbano, Mariangela; Guerrero, Miguel; Zhao, Jian; Velaparthi, Subash; Roberts, Edward; Adrian Saldanha, S.; Chase, Peter; Hodder, Peter; Wang, Zhiwei; Civelli, Olivier; Schaeffer, Marie-Therese; Brown, Steven; Rosen, Hugh Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2012 , vol. 22, # 23 p. 7135 - 7141,7 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Nrf2/p62 signaling in apoptosis resistance and its role in cadmium-induced carcinogenesis.
J. Biol. Chem. 289(41) , 28660-75, (2014) The cadmium-transformed human lung bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells exhibit a property of apoptosis resistance as compared with normal non-transformed BEAS-2B cells. The level of basal reactive oxyg... |
| 4,5-dichloro-2-m-tolyl-2H-pyridazin-3-one |
| 4,5-Dichlor-2-m-tolyl-pyridazin-3-on |
| 4,5-Dichloro-2-(3-methylphenyl)-3(2H)-pyridazinone |
| pyridazinone,2-46 |
| 4,5-Dichloro-2-m-tolylpyridazin-3(2H)-one |