6-Bromohexanoic acid
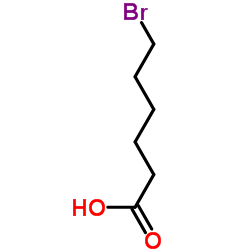
6-Bromohexanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 6-Bromohexanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4224-70-8 | Molecular Weight | 195.054 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 279.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11BrO2 | Melting Point | 32-34 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 67.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 6-bromohexanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 279.2±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 32-34 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11BrO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 195.054 |
| Flash Point | 67.8±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 193.994232 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 1.70 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.490 |
| InChIKey | NVRVNSHHLPQGCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCCCBr |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive |
| Risk Phrases | R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 3261 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 29159080 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2915900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2915900090 other saturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
A Combination of Targeted Sunitinib Liposomes and Targeted Vinorelbine Liposomes for Treating Invasive Breast Cancer.
J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 11 , 1568-82, (2015) Regular chemotherapy cannot eradicate invasive breast cancer cells and the residual cancer cells will form vasculogenic mimicry (VM) channels under hypoxic conditions to provide nutrients for cancer m... |
|
|
Mitochondria apoptosis pathway synergistically activated by hierarchical targeted nanoparticles co-delivering siRNA and lonidamine.
Biomaterials 61 , 178-89, (2015) The mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway is an effective option for cancer therapy due to the presence of cell-suicide weapons in mitochondria. However, anti-apoptotic proteins that are over-expres... |
|
|
Shared Ligands Between Organic Anion Transporters (OAT1 and OAT6) and Odorant Receptors.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43 , 1855-63, (2015) The multispecific organic anion drug transporters OAT6 (SLC22A20) and OAT1 (SLC22A6) are expressed in nasal epithelial cells and both can bind odorants. Sequence analysis of OAT6 revealed an evolution... |
| 6-bromo hexanoic acid |
| EINECS 224-176-5 |
| Hexanoic acid,6-bromo |
| 6-Bromocaproic acid |
| bromopentylcarboxylic acid |
| 6-Bromo-n-caproic acid |
| Hexanoic acid, 6-bromo- |
| 1-bromo-5-carboxypentane |
| 6-Bromohexanoic acid |
| MFCD00004422 |
 CAS#:502-44-3
CAS#:502-44-3 CAS#:4286-55-9
CAS#:4286-55-9 CAS#:6066-82-6
CAS#:6066-82-6 CAS#:55975-26-3
CAS#:55975-26-3 CAS#:1191-25-9
CAS#:1191-25-9 CAS#:57978-00-4
CAS#:57978-00-4 CAS#:42014-54-0
CAS#:42014-54-0 CAS#:629-11-8
CAS#:629-11-8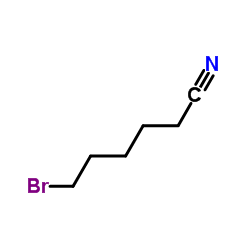 CAS#:6621-59-6
CAS#:6621-59-6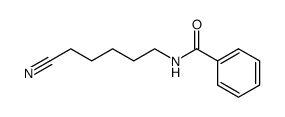 CAS#:642470-70-0
CAS#:642470-70-0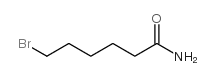 CAS#:57817-55-7
CAS#:57817-55-7 CAS#:5963-14-4
CAS#:5963-14-4 CAS#:5299-60-5
CAS#:5299-60-5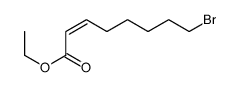 CAS#:141045-76-3
CAS#:141045-76-3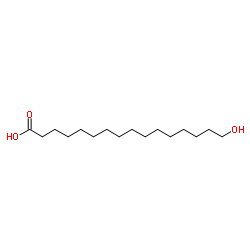 CAS#:506-13-8
CAS#:506-13-8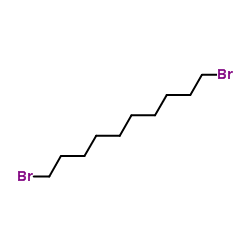 CAS#:4101-68-2
CAS#:4101-68-2 CAS#:26825-90-1
CAS#:26825-90-1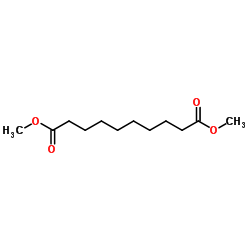 CAS#:106-79-6
CAS#:106-79-6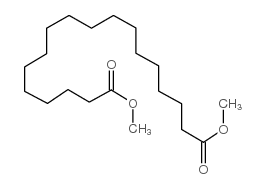 CAS#:1472-93-1
CAS#:1472-93-1
