Diltiazem
Modify Date: 2025-08-23 20:47:39
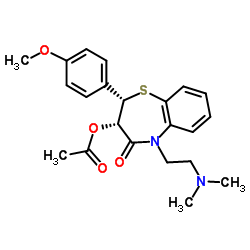
Diltiazem structure
|
Common Name | Diltiazem | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 42399-41-7 | Molecular Weight | 414.518 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 594.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H26N2O4S | Melting Point | 104-106°C (lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 313.3±30.1 °C | |
Use of DiltiazemDiltiazem is an orally active L-type Ca2+ channel blocker, with antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic effects. Diltiazem can be used for the research of cardiac arrhythmia, hypertension, and angina pectoris[1][2][3]. |
| Name | diltiazem |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diltiazem is an orally active L-type Ca2+ channel blocker, with antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic effects. Diltiazem can be used for the research of cardiac arrhythmia, hypertension, and angina pectoris[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
L-type Ca2+ channel[1] |
| In Vitro | Diltiazem (200 µM) in the superfusate, multichannel currents shows a use-dependent decline in amplitude reflecting reductions in the numbers of superpositions of channel openings in isolated guinea pig ventricular myocytes[1]. Diltiazem reduces Ca2+ influx by accelerating inactivation during action potentials, and that the use-dependent blockade is due to increases in the number of channels in a sustained closed state[1]. |
| In Vivo | Diltiazem (100 mg/kg; p.o.; for 4 weeks) prevents aortic aneurysm formation in a blood pressure-independent manner[3]. Diltiazem limits aortic aneurysm formation in mice by a blood pressure–independent anti-inflammatory effect on monocytic cells[3]. Diltiazem (2 mg/kg; i.v.) has t1/2 of 61.2 min, CLel of 3.2 mL/min[4]. Animal Model: Male ApoE−/− mice, angiotensin II induced aneurysms[3] Dosage: 100 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration, in drinking water, for 4 weeks Result: Srongly reduced the vascular remodeling but also lowered the blood pressure. Animal Model: Rat (200-250 g)[4] Dosage: 2 mg/kg (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Administration: Intravenous injection Result: T1/2 (61.2 min), CLel (3.2 mL/min) |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 594.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 104-106°C (lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C22H26N2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 414.518 |
| Flash Point | 313.3±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 414.161316 |
| PSA | 84.38000 |
| LogP | 3.63 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.621 |
| InChIKey | HSUGRBWQSSZJOP-RTWAWAEBSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1ccc(C2Sc3ccccc3N(CCN(C)C)C(=O)C2OC(C)=O)cc1 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| (+)-cis-5-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-(p-methoxyphenyl)-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one Acetate (Ester) |
| Adizem |
| EINECS 255-796-4 |
| d-Diltiazem |
| Citizem |
| Diladel |
| DILTIAZEN |
| Deltazen |
| Adizem XL |
| 1,5-Benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one, 3-(acetyloxy)-5-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, (2S-cis)- |
| (2S,3S)-5-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-yl acetate |
| TILDIEM300LP |
| diltiazemum [INN_la] |
| (2S-cis)-3-(Acetyloxy)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one |
| (+)-cis-Diltiazem |
| (+)-Diltiazem |
| 1,5-Benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one, 3-(acetyloxy)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, (2S-cis)- |
| Dilrene |
| Diltiazem |
| (2S,3S)-5-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-ylacetat |
| 1,5-Benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one, 3-(acetyloxy)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-, (2S,3S)- |
| (2S,3S)-3-(Acetyloxy)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one |
| Cardizen LA |
| MFCD00868239 |
| Coras |
| (2S,3S)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2-[4-(methyloxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-yl acetate |
| Zilden |
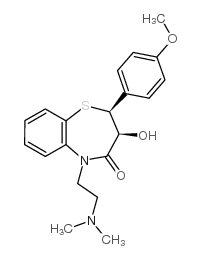 CAS#:42399-40-6
CAS#:42399-40-6 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7 CAS#:4584-46-7
CAS#:4584-46-7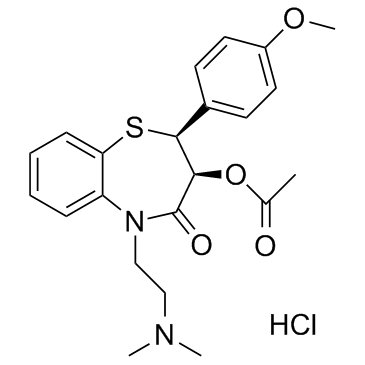 CAS#:33286-22-5
CAS#:33286-22-5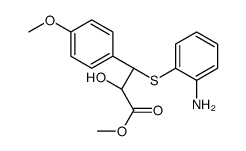 CAS#:99109-07-6
CAS#:99109-07-6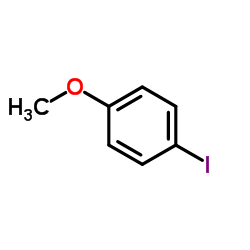 CAS#:696-62-8
CAS#:696-62-8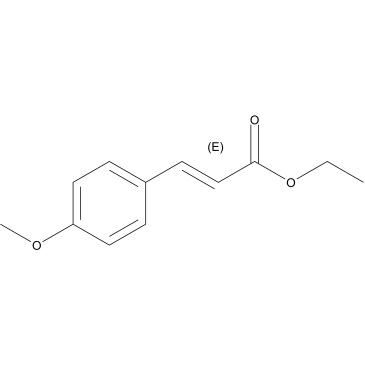 CAS#:24393-56-4
CAS#:24393-56-4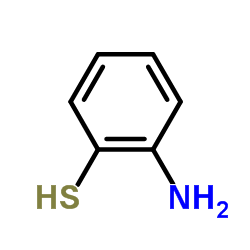 CAS#:137-07-5
CAS#:137-07-5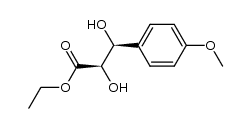 CAS#:182268-43-5
CAS#:182268-43-5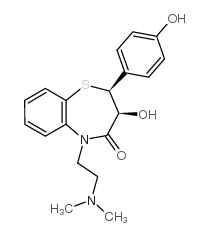 CAS#:84903-82-2
CAS#:84903-82-2