Angiotensin II acetate salt
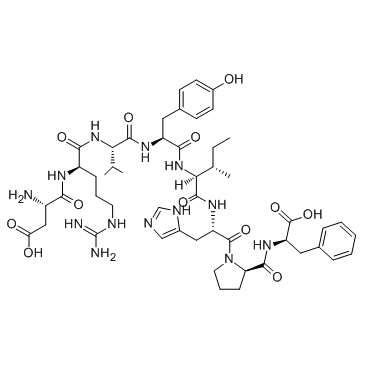
Angiotensin II acetate salt structure
|
Common Name | Angiotensin II acetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4474-91-3 | Molecular Weight | 1046.179 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 809.08°C (rough estimate) | |
| Molecular Formula | C50H71N13O12 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Angiotensin II acetate saltAngiotensin II human is a vasoconstrictor that acts on the AT1 and the AT2 receptor. |
| Name | Angiotensin Ⅱ, human |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Angiotensin II human is a vasoconstrictor that acts on the AT1 and the AT2 receptor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Angiotensin receptor (AT receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Most of the known actions of Angiotensin II (Ang II) are mediated by AT1 receptors, the AT2 receptor contributes to the regulation of blood pressure and renal function[1]. Angiotensin II raises blood pressure (BP) by a number of actions, the most important ones being vasoconstriction, sympathetic nervous stimulation, increased aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Other Angiotensin II actions include induction of growth, cell migration, and mitosis of vascular smooth muscle cells, increased synthesis of collagen type I and III in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. These actions are mediated by type 1 Ang II receptors (AT1)[2]. At the cellular level, responsiveness to Angiotensin II is conferred by the expression of the two classes of angiotensin receptors (AT1 and AT2). The effects of Angiotensin II to increase blood pressure are mediated by AT1 receptors[3]. |
| In Vivo | To distinguish the AT1 receptor population that is critical for the pathogenesis of hypertension, osmotic minipumps are implanted s.c. into each animal to infuse Angiotensin II (1,000 ng/kg/min) continuously for 4 weeks. Angiotensin II causes hypertension by activating AT1 receptors in the kidney promoting sodium reabsorption[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] (129×C57BL/6) F1 mice lacking AT1A receptors for Angiotensin II are used. The mice are fed 10 gm/day gelled 0.25% NaCl diet that contains all nutrients and water. After 1 week of baseline collections, the animals are implanted with osmotic minipumps infusing Angiotensin II and are returned to the metabolic cage for 5 more days. Urinary sodium content is determined by using an IL943 Automatic Flame photometer. After 28 days of Angiotensin II infusion, hearts are harvested, weighed, fixed in formalin, sectioned, and stained with Masson trichrome. All of the tissues are examined by a pathologist (P.R.) without knowledge of genotypes. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 809.08°C (rough estimate) |
| Molecular Formula | C50H71N13O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 1046.179 |
| Exact Mass | 1045.534546 |
| PSA | 406.34000 |
| LogP | 2.34 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.664 |
| InChIKey | CZGUSIXMZVURDU-JZXHSEFVSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(NC(=O)C(Cc1ccc(O)cc1)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(N)CC(=O)O)C(C)C)C(=O)NC(Cc1cnc[nH]1)C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC(Cc1ccccc1)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BW2165000 |
|
Trimethylamine-N-oxide: a carnitine-derived metabolite that prolongs the hypertensive effect of angiotensin II in rats.
Can. J. Cardiol. 30(12) , 1700-5, (2014) Recent evidence suggests that an elevated plasma trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) level is associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events in humans; however, the mechanism is not clea... |
|
|
IGF-1 deficiency impairs cerebral myogenic autoregulation in hypertensive mice.
J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 34(12) , 1887-97, (2014) Aging impairs autoregulatory protection in the brain, exacerbating hypertension-induced cerebromicrovascular injury, neuroinflammation, and development of vascular cognitive impairment. Despite the im... |
|
|
Effects of a domain-selective ACE inhibitor in a mouse model of chronic angiotensin II-dependent hypertension.
Clin. Sci. 127(1) , 57-63, (2014) The somatic isozyme of ACE (angiotensin I-converting enzyme) comprises two distinct zinc-dependent catalytic domains with different substrate specificities for angiotensin I (cleaved selectively by th... |
| Phenylalanine, α-aspartyl-N-(diaminomethylene)ornithylvalyltyrosylisoleucylhistidylprolyl- |
| α-Aspartylarginylvalyltyrosylisoleucylhistidylprolylphenylalanine |
| phenylalanine, α-aspartylarginylvalyltyrosylisoleucylhistidylprolyl- |
| α-aspartyl-N-(diaminomethylidene)ornithylvalyltyrosylisoleucylhistidylprolylphenylalanine |
| α-Aspartyl-N-(diaminomethylene)ornithylvalyltyrosylisoleucylhistidylprolylphenylalanine |
| Angiotensin II |
| ASP-ARG-VAL-TYR-ILE-HIS-PRO-PHE |
| Angiotensin II human |


 CAS#:63-91-2
CAS#:63-91-2 CAS#:51833-78-4
CAS#:51833-78-4
