Atranorin
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 18:14:55
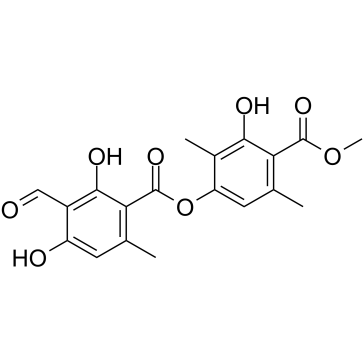
Atranorin structure
|
Common Name | Atranorin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 479-20-9 | Molecular Weight | 374.341 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 535.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18O8 | Melting Point | 156-158ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 189.3±23.6 °C | |
Use of AtranorinAtranorin is a lichen secondary metabolite. Atranorin inhibits lung cancer cell motility and tumorigenesis by affecting AP-1, Wnt, and STAT signaling and suppressing RhoGTPase activity[1][2]. |
| Name | (3-hydroxy-4-methoxycarbonyl-2,5-dimethylphenyl) 3-formyl-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methylbenzoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Atranorin is a lichen secondary metabolite. Atranorin inhibits lung cancer cell motility and tumorigenesis by affecting AP-1, Wnt, and STAT signaling and suppressing RhoGTPase activity[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
RhoGTPase[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 535.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 156-158ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 374.341 |
| Flash Point | 189.3±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 374.100159 |
| PSA | 130.36000 |
| LogP | 6.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.644 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| Atranorine |
| Atranorin |
| 3-Formyl-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methylbenzoic Acid 3-Hydroxy-4-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,5-dimethylphenyl Ester |
| Atranorinsaeure-methylester |
| Parmelin |
| EINECS 207-527-7 |
| Benzoic acid, 3-formyl-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methyl-, 3-hydroxy-4- (methoxycarbonyl)-2,5-dimethylphenyl ester |
| Usnarin |
| Benzoic acid, 3-formyl-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methyl-, 3-hydroxy-4-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,5-dimethylphenyl ester |
| Benzoic acid, 3-formyl-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methyl-, 3-hydroxy-4-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,5-dimethylphenyl ester (9CI) |
| 3-Hydroxy-4-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,5-dimethylphenyl 3-formyl-2,4-dihydroxy-6-methylbenzoate |
| Parmelin acid |
| Atranoric acid |
| Usnarin acid |
| Antranoric acid |
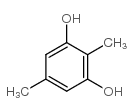 CAS#:488-87-9
CAS#:488-87-9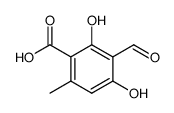 CAS#:479-25-4
CAS#:479-25-4 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1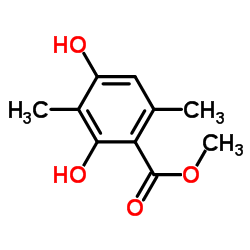 CAS#:4707-47-5
CAS#:4707-47-5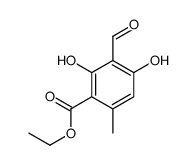 CAS#:39503-14-5
CAS#:39503-14-5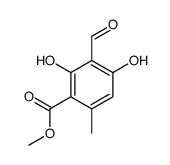 CAS#:34874-90-3
CAS#:34874-90-3 CAS#:62392-82-9
CAS#:62392-82-9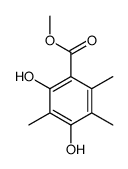 CAS#:34874-78-7
CAS#:34874-78-7 CAS#:34883-04-0
CAS#:34883-04-0
