caffeic acid
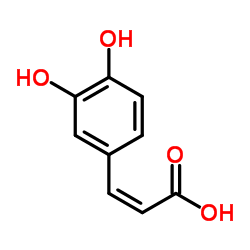
caffeic acid structure
|
Common Name | caffeic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 501-16-6 | Molecular Weight | 180.157 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 416.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 | Melting Point | 211-213ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 220.0±22.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of caffeic acidtrans-Caffeic acid is a growth stimulator that enhances the elongation growth of coleoptile sections[1]. |
| Name | trans-Caffeic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | trans-Caffeic acid is a growth stimulator that enhances the elongation growth of coleoptile sections[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microbial Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 416.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 211-213ºC (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.157 |
| Flash Point | 220.0±22.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 180.042252 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 1.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.707 |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: 50 mg/mL |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P281-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38-40-63-68 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GD8950000 |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
The hepatoprotection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid, major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced oxidative liver damage.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 55 , 92-9, (2013) Perilla frutescens leaves are often used in East Asian gourmet food. In this study, we investigated the hepatoprotective effects of caffeic acid (CA), rosmarinic acid (RA), and their combination. P. f... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents from Commelina communis].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(19) , 3304-8, (2013) To investigate the chemical constituents from Commelina communis, fifteen compounds were separated and purified by silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and ODS column chromatography, and semi-preparative HPLC.... |
|
|
Developmental changes in leaf phenolics composition from three artichoke cvs. (Cynara scolymus) as determined via UHPLC-MS and chemometrics.
Phytochemistry 108 , 67-76, (2014) The metabolomic differences in phenolics from leaves derived from 3 artichoke cultivars (Cynara scolymus): American Green Globe, French Hyrious and Egyptian Baladi, collected at different developmenta... |
| (2Z)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid |
| trans-3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid |
| cis-caffeic acid |
| MFCD00004392 |
| 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid |
| 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-, (2Z)- |
| EINECS 206-361-2 |
| (2Z)-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)acrylic acid |
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-(2E)-2-Propenoic Acid |
| caffeic acid |

