Caffeic acid
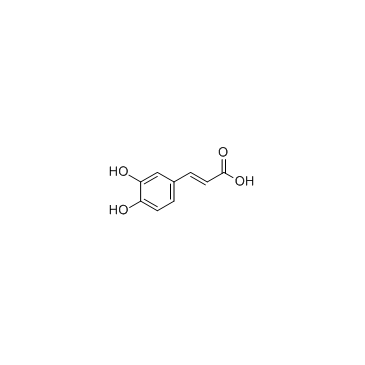
Caffeic acid structure
|
Common Name | Caffeic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 331-39-5 | Molecular Weight | 180.157 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 416.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 | Melting Point | 211-213 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 220.0±22.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Caffeic acidCaffeic acid is an inhibitor of both TRPV1 ion channel and 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO). |
| Name | cis-caffeic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Caffeic acid is an inhibitor of both TRPV1 ion channel and 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Caffeic acid has inhibitory effects on histamine-induced responses and the inhibitory effect of Caffeic acid is gradually increased when the concentration used for pretreatment is increased from 0.1 to 1 mM, similar to typical dose-dependent responses. Pretreatment of HEK293T-TRPV1 cells with 1 mM Caffeic acid results in significant inhibition of capsaicin-induced responses. When lower concentration of Caffeic acid is used, the inhibitory effect for capsaicin-induced responses is less evident. Calcium imaging experiments show that Caffeic acid incubation results in significant inhibition in histamine-sensitive dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Pretreatment with Caffeic acid (1 mM) results in a significant decrease in the percentage of responsive DRG neurons to histamine application from 12.5% to 2.1%. Pretreatment with 1 mM Caffeic acid dramatically blocks the allylisothiocyanate (AITC)-induced intracellular calcium increase in TRPA1-expressing cells. Caffeic acid is also able to block the AITC-induced activation of TRPA1[1]. |
| In Vivo | Mice pretreated with Caffeic acid (500 mg/kg) exhibit significantly less histamine-induced scratching (30.50±10.87 bouts/1 h, n=6). It is further found that the lower dose of Caffeic acid (100 mg/kg) is not significantly effective in terms of anti-scratching effects in histamine-induced scratching, although there appears to be a tendency of reduction (49.40±12.35 bouts/1 h, n=5). The chloroquine induced scratching is significantly inhibited by pretreatment with 500 mg/kg of Caffeic acid (161.6±31.42 bouts/1 h, n=5)[1].Caffeic acid significantly reduces the expression of 5-LO mRNA (P<0.01) dose-dependently in hippocampus. Compare with the ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) non-treated group, 5-LO protein expression is significantly reduced in the I/R-Caffeic acid group (P<0.05 or P<0.01), especially in the I/R-Caffeic acid group (50 mg/kg). Compare with the I/R non-treated group, the latency to find platform is significantly shortened in low- and high-dose Caffeic acid groups, the shortened platform latency is most evident in the I/R- Caffeic acid group (50 mg/kg) (P<0.01). In the low-dose Caffeic acid group, cell injury is still marked, the pyknosis ratio is (63.6±2.8)%, whereas in the high-dose Caffeic acid group, hippocampal neuron karyopyknosis is significantly reduced and the pyknosis ratio is (13.3±3.0)%[2]. |
| Cell Assay | To determine cell viability, MTT assay is performed. HEK293T cells are cultured in 96-well plate at 37°C, a day before so that the confluence of cell is 85 to 90% on the actual day of the experiment. On the day of the experiment the cells are treated with different concentration of Caffeic acid for 10 min. Control cells are treated only with media. After removing supernatant and washing with PBS, MTT reagent (5 mg/mL) is added directly to fresh media. Cells are then incubated at 37°C for additional 4 h followed by draining of the media and overnight storage in dark condition. The next day, DMSO is added to each well and mixed in shaker for 10 min after which plate is read using microplate recorder at 490 nm with a reference wavelength of 620 nm. The relative cell viability (%) is expressed as a percentage relative to the untreated control cells[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats are divided into five groups: the sham group (n=9), ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) non-treated group (n=9), I/R-Caffeic acid group (10 mg/kg) (n=9), I/R-Caffeic acid group (30 mg/kg) (n=9) and I/R- Caffeic acid group (50 mg/kg) (n=9). In I/R-Caffeic acid groups, the rats are administrated Caffeic acid at 10, 30, 50 mg/kg (prepared with 0.3% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) by intraperitoneal injection at 30 min prior to ischemia. The sham group and I/R group are treated with an equal volume of 0.3% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 416.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 211-213 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.157 |
| Flash Point | 220.0±22.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 180.042252 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 1.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.707 |
| InChIKey | QAIPRVGONGVQAS-DUXPYHPUSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)C=Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| Water Solubility | soluble in hot water |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H351-H361 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P281-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38;R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GD8950000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only ... |
|
|
The hepatoprotection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid, major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced oxidative liver damage.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 55 , 92-9, (2013) Perilla frutescens leaves are often used in East Asian gourmet food. In this study, we investigated the hepatoprotective effects of caffeic acid (CA), rosmarinic acid (RA), and their combination. P. f... |
|
|
Effect of selected Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains and different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and polyphenolic composition and sensorial characteristics of Cabernet Sauvignon red wines.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2132-44, (2015) The objective of this work was to study the effect of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains with different capabilities of polysaccharide liberation during alcoholic fermentation in addition to s... |
| CAFFIC ACID |
| Caffeicacid |
| MFCD00004392 |
| 3,4-dihydroxyben |
| 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid,predominantly trans isomer |
| Caffeic |
| 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid |
| EINECS 206-361-2 |
| 3,4-Dihydroxy cinnamic acid |
| CaffeicAcidPure |
| Caffeic acid |
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)acrylic acid |
 CAS#:40918-96-5
CAS#:40918-96-5 CAS#:67879-58-7
CAS#:67879-58-7 CAS#:141-82-2
CAS#:141-82-2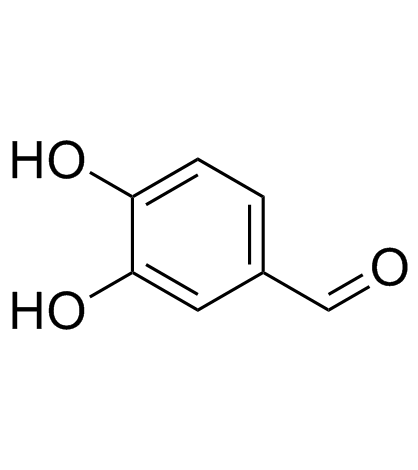 CAS#:139-85-5
CAS#:139-85-5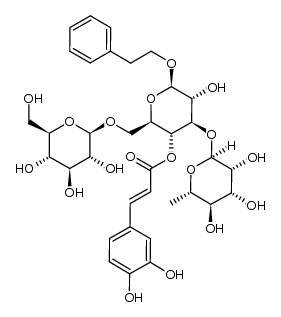 CAS#:1225064-75-4
CAS#:1225064-75-4![delphinidin 3-O-[2-O-(β-xylopyranosyl)-6-O-(trans-caffeoyl)-β-glucopyranoside]-5-O-[6-O-(malonyl)-β-glucopyranoside] Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/458/1346257-27-9.png) CAS#:1346257-27-9
CAS#:1346257-27-9 CAS#:140-10-3
CAS#:140-10-3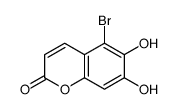 CAS#:143213-06-3
CAS#:143213-06-3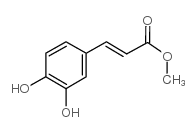 CAS#:3843-74-1
CAS#:3843-74-1 CAS#:22020-28-6
CAS#:22020-28-6 CAS#:120-80-9
CAS#:120-80-9 CAS#:99-50-3
CAS#:99-50-3 CAS#:305-01-1
CAS#:305-01-1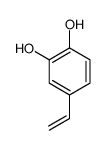 CAS#:6053-02-7
CAS#:6053-02-7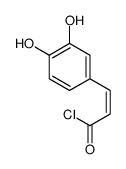 CAS#:23416-69-5
CAS#:23416-69-5
