Oleanic acid
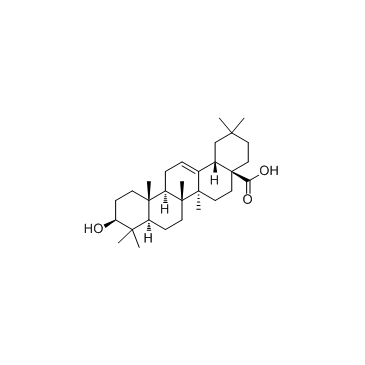
Oleanic acid structure
|
Common Name | Oleanic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 508-02-1 | Molecular Weight | 456.700 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 553.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O3 | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 302.6±26.6 °C | |
Use of Oleanic acidOleanolic acid (Caryophyllin) is a natural compound from plants with anti-tumor activities. |
| Name | oleanolic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Oleanolic acid (Caryophyllin) is a natural compound from plants with anti-tumor activities. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Oleanolic acid (OA) suppresses the proliferation of lung cancer cells in both dose- and time-dependent manners, along with an increase in miR-122 abundance. CCNG1 and MEF2D, two putative miR-122 targets, are found to be downregulated by OA treatment [1]. OA induces autophagy in normal tissue-derived cells without cytotoxicity. OA-induced autophagy is shown to decrease the proliferation of KRAS-transformed normal cells and to impair their invasion and anchorage-independent growth[2]. |
| In Vivo | Mouse model experiments also demonstrat that OA suppresses the growth of KRAS-transformed breast epithelial cell MCF10A-derived tumor xenograft by inducing autophagy [2]. Activation of MAPK pathways, including p-38 MAPK, JNK and ERK, is triggered by OA in both a dose and time-dependent fashion in all the tested cancer cells. OA induces p38 MAPK activation promoted mitochondrial translocation of Bax and Bim, and inhibits Bcl-2 function by enhancing their phosphorylation. OA can induce reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent ASK1 activation, and this event is indispensable for p38 MAPK-dependent apoptosis in cancer cells[3].It is also proved that p38 MAPK knockdown A549 tumors are resistant to the growth-inhibitory effect of OA[3]. In OA-treated EAM mice the number of Treg cells and the production of IL-10 and IL-35 are markedly increased, while proinflammatory and profibrotic cytokines are significantly reduced[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 553.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 456.700 |
| Flash Point | 302.6±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 456.360352 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 9.06 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.557 |
| InChIKey | MIJYXULNPSFWEK-GTOFXWBISA-N |
| SMILES | CC1(C)CCC2(C(=O)O)CCC3(C)C(=CCC4C5(C)CCC(O)C(C)(C)C5CCC43C)C2C1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | RK0177965 |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918199090 other carboxylic acids with alcohol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Analysis of triterpenoids and phytosterols in vegetables by thin-layer chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1381 , 229-38, (2015) Three TLC methods were used for an initial screening of some common plant triterpenoids and phytosterols in cuticular wax extracts of different vegetables (zucchini, eggplant, tomato, red pepper, mang... |
|
|
Functional Characterization of Cucurbitadienol Synthase and Triterpene Glycosyltransferase Involved in Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii.
Plant Cell Physiol. 56 , 1172-82, (2015) Mogrosides, the major bioactive components isolated from the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii, are a family of cucurbitane-type tetracyclic triterpenoid saponins that are used worldwide as high-potency ... |
|
|
Triterpene glycosides and other polar constituents of shea (Vitellaria paradoxa) kernels and their bioactivities.
Phytochemistry 108 , 157-70, (2014) The MeOH extract of defatted shea (Vitellaria paradoxa; Sapotaceae) kernels was investigated for its constituents, and fifteen oleanane-type triterpene acids and glycosides, two steroid glucosides, tw... |
| oleanoic acid |
| Oleanol |
| CARYOPHYLLIN |
| Oleanic acid |
| 3-beta-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid |
| Oleanolicacid |
| Taraligenin |
| Guagenin |
| Araligenin |
| Oleanolic Acid Hydrate |
| MoMorgenin |
| MFCD00064914 |
| Taragenin |
| Gledigeni |
| Oleanolic |
| Oleanolic Acid |
| EINECS 208-081-6 |
 CAS#:1351948-55-4
CAS#:1351948-55-4 CAS#:107387-66-6
CAS#:107387-66-6 CAS#:118800-83-2
CAS#:118800-83-2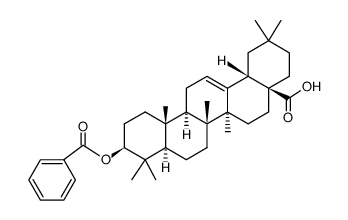 CAS#:6153-31-7
CAS#:6153-31-7 CAS#:152487-59-7
CAS#:152487-59-7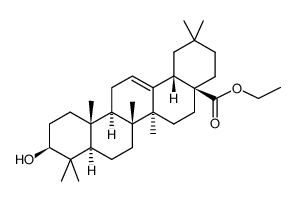 CAS#:110700-49-7
CAS#:110700-49-7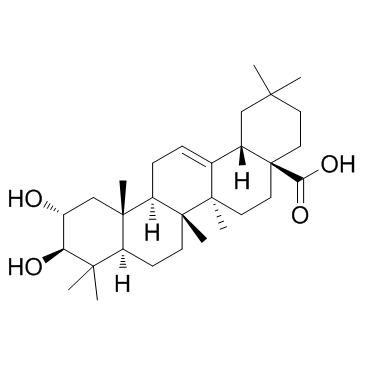 CAS#:4373-41-5
CAS#:4373-41-5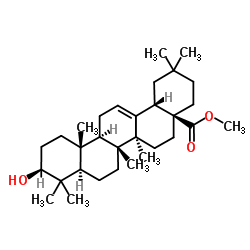 CAS#:1724-17-0
CAS#:1724-17-0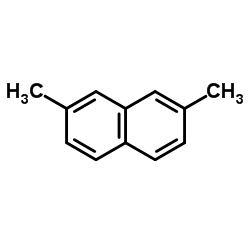 CAS#:582-16-1
CAS#:582-16-1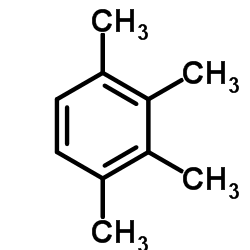 CAS#:488-23-3
CAS#:488-23-3 CAS#:486-34-0
CAS#:486-34-0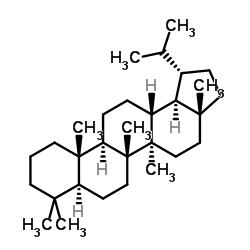 CAS#:471-67-0
CAS#:471-67-0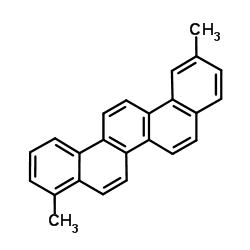 CAS#:1679-02-3
CAS#:1679-02-3 CAS#:303114-51-4
CAS#:303114-51-4 CAS#:25493-94-1
CAS#:25493-94-1
