lead diacetate trihydrate
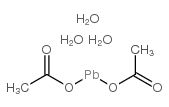
lead diacetate trihydrate structure
|
Common Name | lead diacetate trihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6080-56-4 | Molecular Weight | 379.33400 | |
| Density | 2,55 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 280°C | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H12O7Pb | Melting Point | 75 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 40ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | lead diacetate trihydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 2,55 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 280°C |
| Melting Point | 75 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H12O7Pb |
| Molecular Weight | 379.33400 |
| Flash Point | 40ºC |
| Exact Mass | 380.03500 |
| PSA | 80.29000 |
| Water Solubility | 625 g/L |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360Df-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P308 + P313-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R33;R48/22;R50/53;R61;R62 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 1616 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | OF8050000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29152900 |
|
~% 
lead diacetate ... CAS#:6080-56-4 |
| Literature: Pb: MVol.C2, 189, page 745 - 747 Ullmann (Foerst), 3. Aufl., Bd. 6, 1955, S. 791 |
|
~% 
lead diacetate ... CAS#:6080-56-4 |
| Literature: Chemiker-Zeitung, Chemische Apparatur, vol. 29, p. 1 |
|
~% 
lead diacetate ... CAS#:6080-56-4 |
| Literature: Journal fuer Praktische Chemie (Leipzig), , vol. 7, p. 172 - 181 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 29152900 |
|---|
|
Preventive efficacy of bulk and nanocurcumin against lead-induced oxidative stress in mice.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 152(1) , 31-40, (2013) Chronic lead exposure is associated with several health disorders in humans and animals. Lead exposure leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species and depletes body antioxidant enzymes causing ... |
|
|
Plasmacatalytic removal of lead acetate assisted by precipitation.
Chemosphere 107 , 304-10, (2014) The Gliding Arc Discharge (GAD) is an efficient non-thermal plasma technique able to degrade organic compounds dispersed in water at atmospheric pressure. The degradation of the organometallic lead ac... |
|
|
Nephroprotective effect of calcium channel blockers against toxicity of lead exposure in mice.
Toxicol. Lett. 218(3) , 273-80, (2013) Exposure to lead (Pb) can induce kidney damage, which is related to induction of oxidative damage and disturbance of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Pb can readily permeate through dihydropyridine-... |
| EINECS 206-104-4 |
| Lead acetate trihydrate |
| lead(2+),diacetate,trihydrate |
| MFCD00212528 |



 CAS#:546-67-8
CAS#:546-67-8 CAS#:32812-90-1
CAS#:32812-90-1 CAS#:143314-17-4
CAS#:143314-17-4 CAS#:1120-46-3
CAS#:1120-46-3 CAS#:6598-47-6
CAS#:6598-47-6