Clavulanate potassium
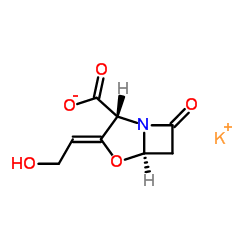
Clavulanate potassium structure
|
Common Name | Clavulanate potassium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 61177-45-5 | Molecular Weight | 237.251 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 545.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8KNO5 | Melting Point | >1600C (dec) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 283.9ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Clavulanate potassiumClavulanate potassium is a potent β-lactamase inhibitor and acts as an antibiotic[1][2]. |
| Name | potassium |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Clavulanate potassium is a potent β-lactamase inhibitor and acts as an antibiotic[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
β-lactamase[1] |
| In Vitro | Clavulanate potassium has weak antibacterial activity against most organisms when administered alone, but given in combination with beta-lactam antibiotics prevents antibiotic inactivation by microbial lactamase[1]. Clavulanate potassium (0.25 mg/L, 0.5 mg/L) causes a relatively slow inhibition of growth, and a higher concentration (1 mg/L) is only marginally more effective than 0.5 mg/L[2]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 545.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >1600C (dec) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8KNO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 237.251 |
| Flash Point | 283.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 237.003952 |
| PSA | 89.90000 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H228-H317-H319-H334 |
| Supplemental HS | Reacts violently with water., Risk of explosion if heated under confinement. |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P261-P280-P284-P304 + P340-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F,Xn,Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 11-42/43-44-36-14 |
| Safety Phrases | 8-16-22-36/37-45-43-26 |
| RIDADR | UN1325 - class 4.1 - PG 2 - Flammable solids, organic, n.o.s., HI: all |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | RN6802700 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
Antibiotics for acute otitis media: yes or no.
JAMA 313(3) , 294-5, (2015)
|
|
|
The NOTA Study (Non Operative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis): prospective study on the efficacy and safety of antibiotics (amoxicillin and clavulanic acid) for treating patients with right lower quadrant abdominal pain and long-term follow-up of conservatively treated suspected appendicitis.
Ann. Surg. 260(1) , 109-17, (2014) To assess the safety and efficacy of antibiotics treatment for suspected acute uncomplicated appendicitis and to monitor the long term follow-up of non-operated patients.Right lower quadrant abdominal... |
|
|
Effect of antimicrobial treatment of acute otitis media on the daily disappearance of middle ear effusion: a placebo-controlled trial.
JAMA Pediatr. 168(7) , 635-41, (2014) Antimicrobial treatment reduces the symptoms of acute otitis media (AOM). The effect of antimicrobial treatment on the duration of middle ear effusion (MEE) and concomitant hearing impairment is not k... |
| Potassium clavulanate |
| EINECS 262-640-9 |
| MFCD01710901 |
| Clavulanic Acid Potassium Salt |
| Clavulanate Potassium |
 CAS#:4744-51-8
CAS#:4744-51-8 CAS#:86917-74-0
CAS#:86917-74-0![2-[5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-6-methylpyrazin-2-yl]ethanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/130/96681-84-4.png) CAS#:96681-84-4
CAS#:96681-84-4 CAS#:96681-85-5
CAS#:96681-85-5 CAS#:87395-84-4
CAS#:87395-84-4
