Ethidium homodimer
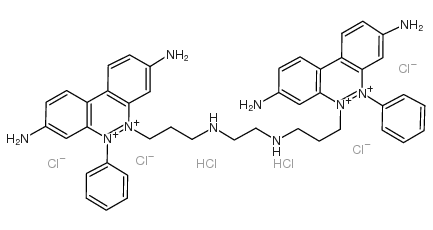
Ethidium homodimer structure
|
Common Name | Ethidium homodimer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 61926-22-5 | Molecular Weight | 931.65300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C44H50Cl6N10 | Melting Point | ≥250ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 85ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Ethidium homodimerEthidium homodimer (EthD-1) is a cell-membrane impermeant nucleic acid fluorochrome with high affinity for DNA. Ethidium homodimer can be used to test cell viability[1]. |
| Name | ethidium homodimer |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ethidium homodimer (EthD-1) is a cell-membrane impermeant nucleic acid fluorochrome with high affinity for DNA. Ethidium homodimer can be used to test cell viability[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Melting Point | ≥250ºC(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C44H50Cl6N10 |
| Molecular Weight | 931.65300 |
| Flash Point | 85ºC |
| Exact Mass | 928.23500 |
| PSA | 143.66000 |
| Storage condition | 20 °C |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H261-H314-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P231 + P232-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310-P422 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2987 8 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
In vivo compatibility of graphene oxide with differing oxidation states.
ACS Nano 9 , 3866-74, (2015) Graphene oxide (GO) is suggested to have great potential as a component of biomedical devices. Although this nanomaterial has been demonstrated to be cytocompatible in vitro, its compatibility in vivo... |
|
|
Enhancing cell migration in shape-memory alginate-collagen composite scaffolds: In vitro and ex vivo assessment for intervertebral disc repair.
J. Biomater. Appl. 29(9) , 1230-46, (2015) Lower lumbar disc disorders pose a significant problem in an aging society with substantial socioeconomic consequences. Both inner tissue (nucleus pulposus) and outer tissue (annulus fibrosus) of the ... |
|
|
Electrospun nanofibrous SF/P(LLA-CL) membrane: a potential substratum for endothelial keratoplasty.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 10 , 3337-50, (2015) Cornea transplant technology has progressed markedly in recent decades, allowing surgeons to replace diseased corneal endothelium by a thin lamellar structure. A thin, transparent, biocompatible, tiss... |
| ethidium chloride homodimer |
| ETHD-1 |
| EthidiumHomodimer(EthD-1) |
| EthD-1,EtDi |
| Ethidium homodimer I solution |
| ETDI |
| 5,5'-[ethylenebis(iminotrimethylene)]bis[3,8-diamino-6-phenylphenanthridinium] dichloride dihydrochloride |
| ETHIDIUM HOMODIMER |