3-Phenylpropiolic acid
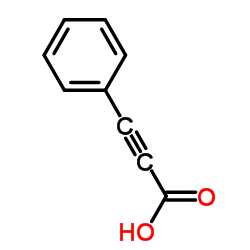
3-Phenylpropiolic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-Phenylpropiolic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 637-44-5 | Molecular Weight | 146.143 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 302.6±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6O2 | Melting Point | 135-137 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 151.0±16.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 3-Phenylpropiolic acidPhenylpropiolic acid is an endogenous metabolite. |
| Name | Phenylpropiolic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Phenylpropiolic acid is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 302.6±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 135-137 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.143 |
| Flash Point | 151.0±16.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 146.036774 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.61 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 |
| InChIKey | XNERWVPQCYSMLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)C#Cc1ccccc1 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Water Solubility | freely soluble |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29163900 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Structure-based design and mechanisms of allosteric inhibitors for mitochondrial branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(24) , 9728-33, (2013) The branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) leucine, isoleucine, and valine are elevated in maple syrup urine disease, heart failure, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. BCAA homeostasis is controlled by the mit... |
|
|
Carbon isotope fractionation in the decarboxylation of phenylpropiolic acid in hydrogen donating media.
Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 37(3) , 239-52, (2001) 13C kinetic isotope effect (KIE) in the decarboxylation of phenylpropiolic acid (PPA) in tetralin medium (Tn) has been determined at 409-432 K and found to be of magnitude similar to the 13C KIE obser... |
|
|
Inactivation of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase by cinnamic acid analogs.
J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 31 , 551-62, (2016) Peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) is a bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the final reaction in the maturation of α-amidated peptide hormones. Peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygena... |
| MFCD00004361 |
| 2-Propynoic acid, 3-phenyl- |
| β-phenylpropargylic acid |
| 3-Phenyl-2-propynoic acid |
| 3-phenyl-propiolic acid |
| phenylpropiolic acid |
| b-phenylpropargylic acid |
| EINECS 211-285-8 |
| 3-Phenylprop-2-ynoic acid |
| phenyl-propiolic acid |
 CAS#:591-50-4
CAS#:591-50-4 CAS#:471-25-0
CAS#:471-25-0 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:536-74-3
CAS#:536-74-3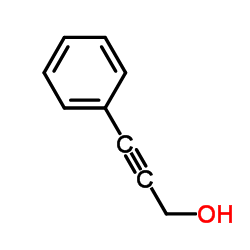 CAS#:1504-58-1
CAS#:1504-58-1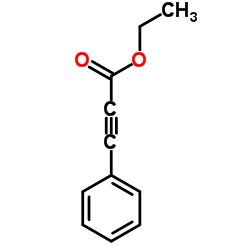 CAS#:2216-94-6
CAS#:2216-94-6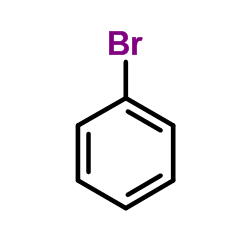 CAS#:108-86-1
CAS#:108-86-1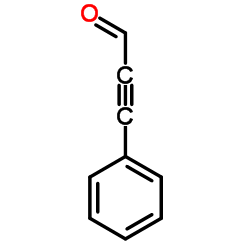 CAS#:2579-22-8
CAS#:2579-22-8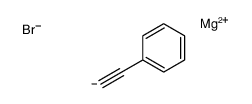 CAS#:6738-06-3
CAS#:6738-06-3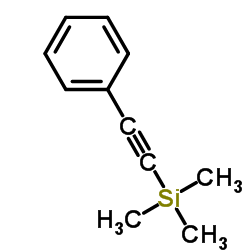 CAS#:2170-06-1
CAS#:2170-06-1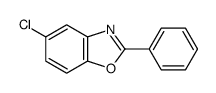 CAS#:1019-90-5
CAS#:1019-90-5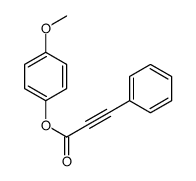 CAS#:104213-86-7
CAS#:104213-86-7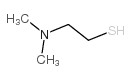 CAS#:108-02-1
CAS#:108-02-1 CAS#:107182-31-0
CAS#:107182-31-0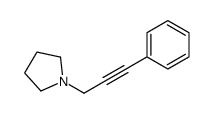 CAS#:1015-02-7
CAS#:1015-02-7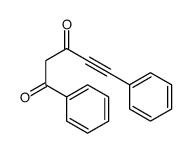 CAS#:107451-76-3
CAS#:107451-76-3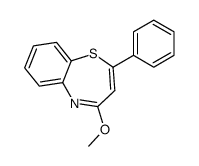 CAS#:104505-69-3
CAS#:104505-69-3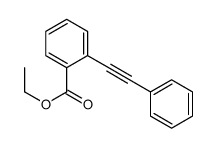 CAS#:110166-71-7
CAS#:110166-71-7 CAS#:4891-38-7
CAS#:4891-38-7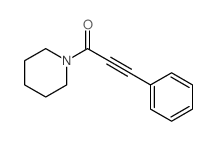 CAS#:14143-92-1
CAS#:14143-92-1
