Sedanolide
Modify Date: 2025-10-23 23:59:48
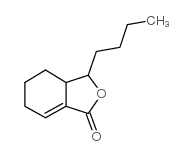
Sedanolide structure
|
Common Name | Sedanolide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6415-59-4 | Molecular Weight | 194.27000 | |
| Density | 1.03 | Boiling Point | 342.0±11.0 °C(Predicted) | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18O2 | Melting Point | 120 °C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of SedanolideSedanolide, a natural compound occurring in edible umbelliferous plants, possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities[1][2]. |
| Name | 3-butyl-3a,4,5,6-tetrahydro-3H-2-benzofuran-1-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sedanolide, a natural compound occurring in edible umbelliferous plants, possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Sedanolide induces autophagy through the PI3K, p53 and NF-κB signaling pathways in human liver cancer cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Sedanolide increases the activity of glutathione-S-transferase (GST) in the liver, small intestinal mucosa, and forestomach of A/J mice[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.03 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 342.0±11.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Melting Point | 120 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 194.27000 |
| Exact Mass | 194.13100 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 2.82850 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.742 |
| InChIKey | UPJFTVFLSIQQAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCC1OC(=O)C2=CCCCC21 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| Neocnidilide |
| 3-butyl-3a,4,5,6-tetrahydro-3H-isobenzofuran-1-one |
| Sedanolide |
| MFCD00171327 |