Chlorprothixene hydrochloride
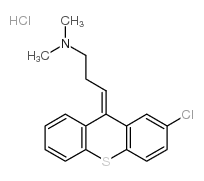
Chlorprothixene hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Chlorprothixene hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6469-93-8 | Molecular Weight | 352.32100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 461.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H19Cl2NS | Melting Point | 221ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 233.1ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Chlorprothixene hydrochlorideChlorprothixene hydrochloride is a dopamine and histamine receptors antagonist with Kis of 18 nM, 2.96 nM, 4.56 nM, 9 nM and 3.75 nM for hD1, hD2, hD3, hD5 and hH1 receptors, respectively. Antipsychotic activity[1]. |
| Name | 2-Chloro-9-(3-dimethylaminopropylidene)thioxanthene hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chlorprothixene hydrochloride is a dopamine and histamine receptors antagonist with Kis of 18 nM, 2.96 nM, 4.56 nM, 9 nM and 3.75 nM for hD1, hD2, hD3, hD5 and hH1 receptors, respectively. Antipsychotic activity[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human D1 Receptor:18 nM (Ki) Human D2 Receptor:2.96 nM (Ki) Human D3 Receptor:4.56 nM (Ki) Human D5 Receptor:9 nM (Ki) Human H1 Receptor:3.75 nM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Chlorprothixene binds to 5-HT receptors with pKis of 8.3, 8.5, and 9.4 for 5-HT7, 5-HT6 and 5-HT2, respectively[2]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 461.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 221ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H19Cl2NS |
| Molecular Weight | 352.32100 |
| Flash Point | 233.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 351.06200 |
| PSA | 28.54000 |
| LogP | 5.99000 |
| InChIKey | YWKRLOSRDGPEJR-KIUKIJHYSA-N |
| SMILES | CN(C)CCC=C1c2ccccc2Sc2ccc(Cl)cc21.Cl |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water and in alcohol, slightly soluble in methylene chloride. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | 36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | XO0610000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
Spatial receptive fields in the retina and dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of mice lacking rods and cones.
J. Neurophysiol. 114 , 1321-30, (2015) In advanced retinal degeneration loss of rods and cones leaves melanopsin-expressing intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) as the only source of visual information. ipRGCs drive... |
|
|
Characterization of the commercially-available fluorescent chloroquine-BODIPY conjugate, LynxTag-CQGREEN, as a marker for chloroquine resistance and uptake in a 96-well plate assay.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e110800, (2014) Chloroquine was a cheap, extremely effective drug against Plasmodium falciparum until resistance arose. One approach to reversing resistance is the inhibition of chloroquine efflux from its site of ac... |
|
|
Biologically active conformers of phenothiazines and thioxanthenes. Further evidence for a ligand model of dopamine D2 receptor antagonists.
J. Med. Chem. 36 , 2219-2227, (1993) Conformational analyses have been performed on several phenothiazine and thioxanthene dopamine antagonists using the MM2-87 program and parameter set. The compounds that were examined are thioridazine... |
| Chlorprothixene hydrochloride |