Forskolin

Forskolin structure
|
Common Name | Forskolin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 66575-29-9 | Molecular Weight | 410.501 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 519.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H34O7 | Melting Point | 282-232ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 171.8±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ForskolinForskolin is a potent adenylate cyclase activator, with IC50 and EC50 of 41 nM and 0.5 μM for type I adenylyl cyclase, respectively. |
| Name | forskolin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Forskolin is a potent adenylate cyclase activator, with IC50 and EC50 of 41 nM and 0.5 μM for type I adenylyl cyclase, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 41 nM (Adenylyl cyclase)[1] EC50: 0.5 μM (Adenylyl cyclase)[1] |
| In Vitro | Forskolin (Fsk) is a naturally occurring diterpene isolated from Coleus forskholii, directly activates adenylyl cyclase (AC) through its catalytic subunit to increase intracellular levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)[1]. Forskolin (Fsk) affects the proliferation of the human T-cell lines such as Kit 225 and MT-2. Forskolin treatment inhibits the proliferation of both Kit 225 and MT-2 cells in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 equal to ~5 μM Fsk. Forskolin treatment (10-100 μM) increases cAMPi levels ~5- to 20-fold above basal levels, which reache maximum levels between 50-100 μM Forskolin[2]. |
| In Vivo | The Forskolin (Fsk)-treated Mrp4-/- mice shows an increased number of Ki67-positive and cleaved caspase 3-positive ECs, a significant decrease in the amount of pericyte coverage, and a reduced number of empty sleeves. In pups exposed to hyperoxia (75% oxygen) from P7 to P12, the Mrp4-/- mice shows a significant increase in the unvascularized retinal area[3]. The average blood glucose in the healthy rat group is 102.12±1.94 mg/dL, 101.25±3.56 for control group and 103±2.08 in forskolin group. The data shows that glucose levels at the end of the study are lower in forskolin group, with a significant difference according to the statistical tests applied (p=0.03)[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | For Jak3 kinase assays, Fsk-treated MT-2 cells are lysed, clarified, and immunoprecipitated using Jak3 antibody. Kinase reactions are carried out at 30°C for 20 min. For PKA kinase assays, untreated MT-2 cells are lysed, and Jak3 is immunoprecipitated and bound to PAS beads. Immunoprecipitated Jak3 is washed with kinase buffer (50 mM Hepes-NaOH (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM DTT, 20 μg/mL aprotinin, 10 μg/mL leupeptin, 1 μg/mL pepstatin A) and incubated with 200 μM ATP and purified protein kinase A catalytic subunit (PKAc) as indicated in the figure legends. Kinase reactions are carried out at 32 °C for 30 min followed by vigorous washing of the beads with cold kinase wash buffer. For [γ-32P]ATP radiolabeled kinase assays using recombinant Jak3, Hek293 cells are transfected with wild type (WT) Jak3 or kinase-dead Jak3 K855A using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells are lysed and immunoprecipitated with Jak3 antibody. Jak3-bound PAS beads are washed three times in cold lysis buffer followed by kinase buffer. Kinase reactions are initiated by adding 10 μCi [γ-32P]ATP, 10 μM unlabeled ATP, and 1 μg of purified PKAc to Jak3-bound PAS bead reaction mixtures. Kinase reactions are performed at 32°C for 30 min. Jak3-bound PAS beads are washed three times in radioimmunoassay buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 75 mM NaCl, 20 mM EDTA, 10 mM EGTA, 20 mM Na4P2O7, 50 mM NaF, 20 mM 2-glycerolphosphate, 1 mM p-nitrophenylphosphate, 0.1% Triton X-100) and one time in kinase wash buffer. The reactions are stopped by adding 2× SDS-PAGE sample buffer followed by SDS-PAGE. Coomassie stainable Jak3 bands are excised from the PVDF membrane and subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Quiescent Kit 225 or MT-2 cells are seeded into 96-well plates at 5×104 cells per well. Cells are then pretreated for 1 h with 1% DMSO (vehicle) or Forskolin at 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 μMconcentrations. The cells are stimulated with IL-2 and cultured for an additional 20 h at 37°C. Control cells are treated with 1% DMSO for 20 h. During the final 4 h of incubation, the cells are pulsed with [3H]thymidine at a concentration of 0.5 μCi/200 μL. Cells are harvested onto fiberglass filters and analyzed using liquid scintillation counting[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] C57BL/6J mice are used. Mrp4-knockout mice, which are established and repeatedly backcrossed to the C57BL/6J mice. Forskolin is injected intraperitoneally into neonatal mice at postnatal days 4 (P4) and 5 (P5). Mice injected with DMSO serve as the controls. The treated mice are euthanized at P6, and their retinas are isolated for whole-mount immunohistochemistry (IHC). The effect of different concentrations of Forskolin on the survival rate and retinal vasculature is first tested, and the optimal concentration is determined, 1.0 μg/50 μL (0.3 mg/kg) at P4 and 1.5 μg/50 μL (0.5 mg/kg) at P5, used to compare the retinal vascular phenotypes between WT mice and Mrp4-deficient mice. Rats[4] Male Wistar rats, aged 10-14 weeks old, with a mean weight of 300 g±50 g, are divided into four groups; 19 are experimentally induced to develop diabetes, and 8 are maintained in a healthy condition. Both diabetic and healthy rats receive no Forskolin (control), or 6 mg/kg per day of Forskolin, administered orally for 8 weeks. Blood glucose levels are determined in each group before and after Forskolin treatment. The diabetic rats are tested two weeks after confirming the presence of diabetes (three weeks after the induction) and after eight weeks of the designated treatment. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 519.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 282-232ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H34O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 410.501 |
| Flash Point | 171.8±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 410.230438 |
| PSA | 113.29000 |
| LogP | 3.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.552 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
The activity of cAMP-phosphodiesterase 4D7 (PDE4D7) is regulated by protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation within its unique N-terminus.
FEBS Lett. 589(6) , 750-5, (2015) The cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases type 4 (PDE4s) are expressed in a cell specific manner, with intracellular targeting directed by unique N-terminal anchor domains. All long form PDE4s are phosphoryla... |
|
|
ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates endothelin-1-induced lipolysis in adipocytes.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 90(4) , 406-13, (2014) Endothelin-1 (ET-1) induces lipolysis in adipocytes, where ET-1 chronic exposure results in insulin resistance (IR) through suppression of glucose transporter (GLUT)4 translocation to the plasma membr... |
|
|
OSBP-related protein 3 (ORP3) coupling with VAMP-associated protein A regulates R-Ras activity.
Exp. Cell Res. 331(2) , 278-91, (2015) ORP3 is an R-Ras interacting oxysterol-binding protein homolog that regulates cell adhesion and is overexpressed in several cancers. We investigated here a novel function of ORP3 dependent on its targ... |
| (3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-6,10,10b-Trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1-oxo-3-vinyldodecahydro-1H-benzo[f]chromen-5-yl acetate |
| (3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-3-ethenyl-6,10,10b-trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1-oxododecahydro-1H-benzo[f]chromen-5-yl acetate |
| HL 362 |
| (3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-6,10,10b-Trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1-oxo-3-vinyldodecahydro-1H-benzo[f]chromen-5-ylacetat |
| EINECS 266-410-9 |
| Coleonol |
| 1H-Naphtho[2,1-b]pyran-1-one, 5-(acetyloxy)-3-ethenyldodecahydro-6,10,10b-trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-, (3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)- |
| L 75-1362B |
| Forskolin |
| ForsLean |
| FORSKOHLIN |
| boforsin |
| [3H]-Forskolin |
| COLFORSIN |
| MFCD00082317 |
 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7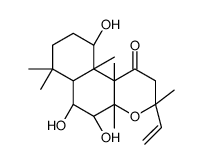 CAS#:64657-20-1
CAS#:64657-20-1![(1S,6S,11S,12S,2R)-14-methoxy-1,4,4,8,8,12,16-heptamethyl-3,5,17-trioxa-16-vinyltetracyclo[11.4.0.0.2,607,12]heptadec-14-en-11-ol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/024/115155-11-8.png) CAS#:115155-11-8
CAS#:115155-11-8![(1S,6S,11S,12S,2R,16R)-14-methoxy-1,4,4,8,8,12,16-heptamethyl-3,5,17-trioxa-16-vinyltetracyclo[11.4.0.02,607,12]heptadec-13-en-11-ol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/417/115155-09-4.png) CAS#:115155-09-4
CAS#:115155-09-4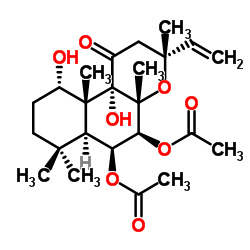 CAS#:81873-08-7
CAS#:81873-08-7
