agaric acid
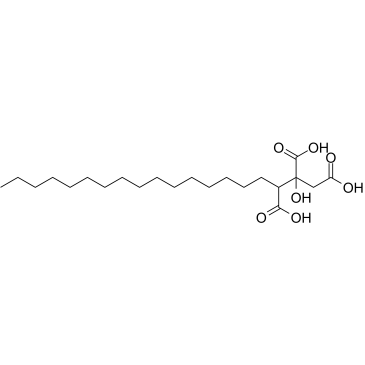
agaric acid structure
|
Common Name | agaric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 666-99-9 | Molecular Weight | 416.54900 | |
| Density | 1.115g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 509.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H40O7 | Melting Point | 142° (dec) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 275.9ºC | |
Use of agaric acidAgaric acid (Agaricinic Acid) is obtained from various plants of the fungous tribe, i.e. Polyporus officinalis and Polyporus igniarius. Agaric acid induces mitochondrial permeability transition through its interaction with the adenine nucleotide translocase. Agaric acid promotes efflux of accumulated Ca2+, collapse of transmembrane potential, and mitochondrial swelling. Agaric acid is used to regulate lipid metabolism[1]. |
| Name | 2-hydroxynonadecane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Agaric acid (Agaricinic Acid) is obtained from various plants of the fungous tribe, i.e. Polyporus officinalis and Polyporus igniarius. Agaric acid induces mitochondrial permeability transition through its interaction with the adenine nucleotide translocase. Agaric acid promotes efflux of accumulated Ca2+, collapse of transmembrane potential, and mitochondrial swelling. Agaric acid is used to regulate lipid metabolism[1]. |
|---|---|
| References |
| Density | 1.115g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 509.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 142° (dec) |
| Molecular Formula | C22H40O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 416.54900 |
| Flash Point | 275.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 416.27700 |
| PSA | 132.13000 |
| LogP | 4.84900 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.501 |
| InChIKey | HZLCGUXUOFWCCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(C(=O)O)C(O)(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RA5365000 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
|
Agaric acid induces mitochondrial permeability transition through its interaction with the adenine nucleotide translocase. Its dependence on membrane fluidity.
Mitochondrion 5 , 272-281, (2005) The effect of agaric acid as inducer of mitochondrial permeability transition was studied. It was found that: (i) agaric acid (AA) promoted efflux of accumulated Ca2+, collapse of transmembrane potent... |
|
|
The mechanisms of fatty acid-induced proton permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane.
J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 31 , 447-455, (1999) Nonesterified long-chain fatty acids have long been known as uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. They are efficient protonophores in the inner mitochondrial membrane but not so in artificial phos... |
|
|
The effect of N-ethylmaleimide on permeability transition as induced by carboxyatractyloside, agaric acid, and oleate.
Cell Biochem. Biophys. 51 , 81-87, (2008) In this work, we studied the effect of N-ethylmaleimide on permeability transition. The findings indicate that the amine inhibited the effects of carboxyatractyloside and agaric acid. It is known that... |
| Laricic acid |
| n-Hexadecylcitric acid |
| EINECS 211-566-5 |
| Agaricinic acid |
| (2S,3S)-2-Hydroxy-nonadecan-1,2,3-tricarbonsaeure |
| Lr-2-Hydroxy-nonadecan-1,2rF,3cF-tricarbonsaeure |
| Agaric acid |
| Agaricinsaeure |
| MFCD00002665 |
| Agaricin |
| (2S,3S)-2-Hydroxy-nonadecan-1,2,3-tricarbonsaeure (Agaricinsaeure) |
| Agaricic acid |
| (2S,3S)-2-hydroxy-nonadecane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
 CAS#:629-66-3
CAS#:629-66-3 CAS#:71595-37-4
CAS#:71595-37-4 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7 CAS#:57-11-4
CAS#:57-11-4