Thapsigargin
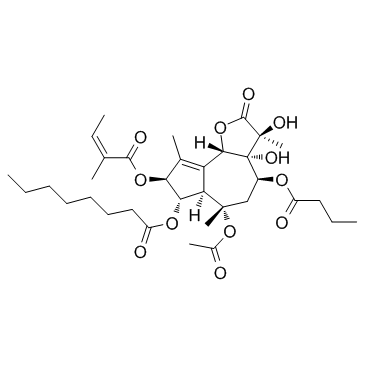
Thapsigargin structure
|
Common Name | Thapsigargin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67526-95-8 | Molecular Weight | 650.754 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 699.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C34H50O12 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 209.0±25.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of ThapsigarginThapsigargin is an inhibitor of microsomal Ca2+-ATPase. |
| Name | thapsigargin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Thapsigargin is an inhibitor of microsomal Ca2+-ATPase. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ca2+-ATPase[1] |
| In Vitro | Thapsigargin inhibits Ca2+ entry into human neutrophil granulocytes[1]. Thapsigargin inhibits the carbachol-evoked [Ca2+]i-transients with (IC50=0.353 nM) or without (IC50=0.448 nM) a KCl-prestimulation, but an additional small component, with a much lower sensitivity (IC50=4814 nM), is observed in the absence of a KCl-prestimulation. In contrast, the KCl-evoked [Ca2+]i-transients displayed only one component with a very low sensitivity to Thapsigargin in both absence (IC50=3343 nM) and presence (IC50=6858 nM) of a carbachol-prestimulation[2]. To determine whether hepatitis B virus (HBV) affects cell survival and apoptosis, the HepG2.2.15 and HepG2 cells are treated with 500 nM Thapsigargin (TG) or PBS for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h and cell proliferation is detected using the MTT assay. Thapsigargin inhibitscell growth in a time-dependent manner, especially in the HepG2 cells, for which 64% cell growth is inhibited at 96 h compared with 45% in the HepG2.2.15 cells (P<0.001). Similarly, at 24, 48 and 72 h, greater inhibition is observed for the HepG2 cells than for HepG2.2.15 cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | To assess endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in vivo, interperitoneal injection of either Thapsigargin (TG; 0.5 ug/g/body weight) or Tunicamycin (TUN; 1 ug/g/body weight) is performed in mice. Thapsigargin at a dose of 0.5 ug/g/body weight is safe and does not elicit any adverse effects on survival in these mice. The induction of ER stress in the liver and adipose tissue of mice treated with either Thapsigargin or TUN is then examined, by assessing the expression of key ER stress and UPR markers. Both Thapsigargin and TUN treatment in mice results in significant expression of ER stress markers ATF6 and eIF2α in adipose tissue (p<0.05)[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The HepG2 or HepG2.2.15 cells are seeded at a density of 5×103 cells/well in 96-well plates. The cells are treated with 500 nM Thapsigargin for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h and cells treated with PBS are used as controls. Subsequent to the end of each time point, the cells are incubated with 10 µL MTT for 4 h at 37°C in the dark. The supernatant is removed and 100 µL DMSO is used for dissolution. A Synergy H1 microplate reader is used to measure absorbance at 490 nm. All experiments are performed in triplicate and repeated 3 times[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] Male Balb/c mice (20-25g) are injected intraperitoneally with Tunicamycin solution (1 μg/g body mass). For Thapsigargin solution a dose response is conducted using (0.25 ug/g, 0.5 ug/g and 1 ug/g body mass). As controls, mice are injected intraperitoneally with control buffer (150 mM dextrose containing 1% DMSO). Adipose and liver tissues are harvested 24 hrs post treatment[4]. |
| References |
[4]. Abdullahi A, et al. Modeling Acute ER Stress in Vivo and in Vitro. Shock. 2017 Apr;47(4):506-513. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 699.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C34H50O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 650.754 |
| Flash Point | 209.0±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 650.330200 |
| PSA | 171.96000 |
| LogP | 6.61 |
| Appearance of Characters | liquid or film |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.540 |
| InChIKey | IXFPJGBNCFXKPI-FSIHEZPISA-N |
| SMILES | CC=C(C)C(=O)OC1C(C)=C2C(C1OC(=O)CCCCCCC)C(C)(OC(C)=O)CC(OC(=O)CCC)C1(O)C2OC(=O)C1(C)O |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . R42:May cause sensitization by inhalation. |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Novel role for TRPC4 in regulation of macroautophagy by a small molecule in vascular endothelial cells.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853(2) , 377-87, (2015) Macroautophagy (autophagy) is an important factor affecting the function of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and must be tightly regulated in these cells. However, the precise mechanisms underlying t... |
|
|
Identification of the cellular mechanisms that modulate trafficking of frizzled family receptor 4 (FZD4) missense mutants associated with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(6) , 3423-31, (2014) Fifteen missense mutations in the frizzled family receptor 4 (FZD4) reported to cause familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR) were evaluated to establish the pathological cellular mechanism of dis... |
|
|
Improved plasma membrane expression of the trafficking defective P344R mutant of muscle, skeletal, receptor tyrosine kinase (MuSK) causing congenital myasthenic syndrome.
Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 60 , 119-29, (2015) Muscle, skeletal, receptor tyrosine kinase (MuSK) is a key organizer at the postsynaptic membrane and critical for proper development and maintenance of the neuromuscular junction. Mutations in MUSK r... |
| Pamoic acid disodium salt |
| Octanoic acid, (3S,3aR,4S,6S,6aR,7S,8S,9bS)-6-(acetyloxy)-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,7,8,9b-decahydro-3,3a-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethyl-8-[[(3Z)-3-methyl-1-oxo-3-penten-1-yl]oxy]-2-oxo-4-(1-oxobutoxy)azuleno[4,5-b]furan-7-yl ester |
| (3S,3aR,4S,6S,6aR,7S,8S,9bS)-6-Acetoxy-4-(butyryloxy)-3,3a-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethyl-8-{[(3Z)-3-methyl-3-pentenoyl]oxy}-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,7,8,9b-decahydroazuleno[4,5-b]furan-7-yl octanoate |
| sesquiterpene lactone tetraester |
| Thallium mononitrate |
| thallous nitrate TlNO3,orthorhombic |
| Thapsigargin |
| MFCD00083511 |
| THALLIUM NITRATE |
| THALLOUS NITRATE |
| rcrawastenumberu217 |
| thallous |
| sesquiterpene lactone |
| Thapsigargin,(3S,3aR,4S,6S,6AR,7S,8S,9bS)-6-(Acetyloxy)-2,3,3a,4,5,6,6a,7,8,9b-decahydro-3,3a-dihydroxy-3,6,9-trimethyl-8-[[(2Z)-2-methyl-1-oxo-2-butenyl]oxy]-2-oxo-4-(1-oxobutoxy)azuleno[4,5-b]furan-7-yloctanoate |

