Cinnamic acid, p-chloro-.alpha.-cyano-
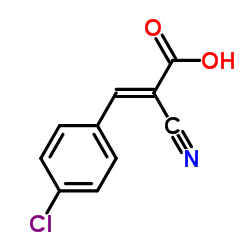
Cinnamic acid, p-chloro-.alpha.-cyano- structure
|
Common Name | Cinnamic acid, p-chloro-.alpha.-cyano- | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69727-07-7 | Molecular Weight | 207.613 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 377.0±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H6ClNO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 181.8±25.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Cinnamic acid, p-chloro-.α.-cyano |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 377.0±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C10H6ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 207.613 |
| Flash Point | 181.8±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 207.008713 |
| PSA | 61.09000 |
| LogP | 2.59 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.642 |
| InChIKey | MXCRRKYUQNHWLJ-YVMONPNESA-N |
| SMILES | N#CC(=Cc1ccc(Cl)cc1)C(=O)O |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P301 + P310 |
| RIDADR | UN 3439 6.1 / PGIII |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
|
4-Chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid is an advanced, rationally designed MALDI matrix.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105(34) , 12200-5, (2008) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) has become an enabling technology for the fields of protein mass spectrometry (MS) and proteomics. Despite its widespread use, for example, in prote... |
|
|
Ion yields in UV-MALDI mass spectrometry as a function of excitation laser wavelength and optical and physico-chemical properties of classical and halogen-substituted MALDI matrixes.
Anal. Chem. 84(15) , 6567-76, (2012) The laser wavelength constitutes a key parameter in ultraviolet-matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-mass spectrometry (UV-MALDI-MS). Optimal analytical results are only achieved at laser wavel... |
|
|
The new matrix 4-chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid allows the detection of phosphatidylethanolamine chloramines by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20(5) , 867-74, (2009) Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) are abundant lipid constituents of the cellular membrane. The amino group of PEs exhibits high reactivity with hypochlorous acid that is generated under inflammatory co... |
| trans-3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-cyanoprop-2-enoic acid |
| (2E)-3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-cyano-2-propenoic Acid |
| (2E)-3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-cyanoacrylic acid |
| (E)-2-Cyano-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)acrylic Acid |
| 2-Propenoic acid, 3- (4-chlorophenyl)-2-cyano- |
| 2-Propenoic acid, 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-cyano-, (2E)- |
| Cinnamic acid, p-chloro-α-cyano- |
| 4-Chlor-benzalmalonsaeure-mononitril |
| 3-(4-Chlor-phenyl)-2-cyan-acrylsaeure |
| 3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-2-cyano-acrylic acid |
 CAS#:126245-52-1
CAS#:126245-52-1 CAS#:54440-99-2
CAS#:54440-99-2