2,4-DICHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID SODIUM
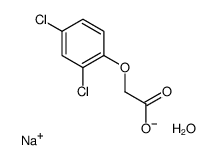
2,4-DICHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID SODIUM structure
|
Common Name | 2,4-DICHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID SODIUM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7084-86-8 | Molecular Weight | 261.03500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 345.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7Cl2NaO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 162.8ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Sodium (2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetate hydrate (1:1:1) |
|---|
| Boiling Point | 345.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H7Cl2NaO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 261.03500 |
| Flash Point | 162.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 259.96200 |
| PSA | 58.59000 |
| LogP | 1.05780 |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H318-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
|
Why plants need more than one type of auxin.
Plant Sci. 180 , 454-460, (2011) The versatile functionality and physiological importance of the phytohormone auxin is a major focus of attention in contemporary plant science. Recent studies have substantially contributed to our und... |
|
|
Arabidopsis FAB1A/B is possibly involved in the recycling of auxin transporters.
Plant Signal Behav. 6 , 583-585, (2011) Fab1/PIKfyve produces Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns (3,5) P2) from Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns 3-P), and is involved not only in vacuole/lysosome homeostasis, but also in ... |
|
|
Initiation of somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of oocarpa pine (Pinus oocarpa Schiede ex Schlectendal).
Tree Physiol. 31 , 539-554, (2011) The focus of the current project was to establish somatic embryogenesis protocols for the tropical pine species Pinus oocarpa using immature zygotic embryos (ZEs) as explants. Somatic embryogenesis is... |

