α-Aminoadipic acid
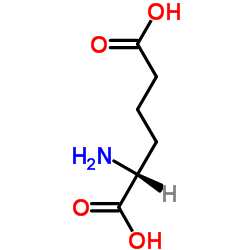
α-Aminoadipic acid structure
|
Common Name | α-Aminoadipic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7620-28-2 | Molecular Weight | 161.156 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 364.0±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11NO4 | Melting Point | 208-210 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 173.9±25.1 °C | |
| Name | D-2-aminoadipic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 364.0±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208-210 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 161.156 |
| Flash Point | 173.9±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 161.068802 |
| PSA | 100.62000 |
| LogP | -0.54 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Inhibition of the glutamate transporter and glial enzymes in rat striatum by the gliotoxin, alpha aminoadipate.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 113 , 536-540, (1994) 1. The effect of the gliotoxic analogue of glutamate, alpha aminoadipate, on the high affinity transport of D-[3H]-aspartate into a crude striatal P2 preparation, and on the activity of two enzymes of... |
|
|
The glio-toxic mechanism of alpha-aminoadipic acid on cultured astrocytes.
J. Neurocytol. 27 , 109, (1998) The mechanism of action of the glutamate analogue alpha-aminoadipic (AAA) acid was investigated in terms of its toxicity to cultured astrocytes. AAA was more toxic to type 1 astrocytes than type 2 ast... |
|
|
The effects of D-alpha-aminoadipic acid on long-term potentiation in the hippocampus of the rat in vitro.
J. Neurosci. Res. 24 , 139-150, (1996) Many studies on long-term potentiation (LTP) in hippocampal region CA1 focus on receptor-mediated events that are often presumed to be linked to postsynaptic processes. Whereas it is now well-known th... |
| 2-Aminohexanedioic acid |
| 2-aminoadipic acid |
| AAD |
| DL-2-Aminohexanedioic acid |
| Hexanedioic acid, 2-amino-, (2R)- |
| D-2-Aminoadipic Acid |
| D-2-AMINOADIPIC ACID 98 |
| Hexanedioic acid, 2-amino- |
| α-Amino-adipic acid |
| .α.-Aminoadipic acid |
| UNII:1K7B1OED4N |
| DL-2-Aminoadipic acid |
| DL-a-aminoadipic acid |
| D-aminohexanoic diacid |
| D-Homoglutamic acid |
| a-Aminoadipic acid |
| (2R)-2-Aminohexanedioic acid |
| H-D-2-Aad-OH |
| (±)-2-Aminoadipic acid |
| D-a-Aminoadipic acid |
| MFCD00063118 |
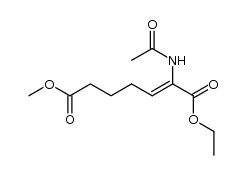 CAS#:156386-97-9
CAS#:156386-97-9 CAS#:119825-45-5
CAS#:119825-45-5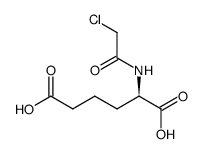 CAS#:71301-34-3
CAS#:71301-34-3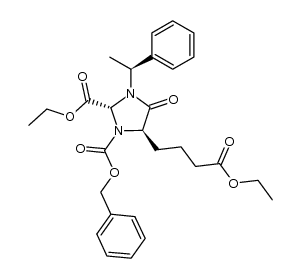 CAS#:149253-60-1
CAS#:149253-60-1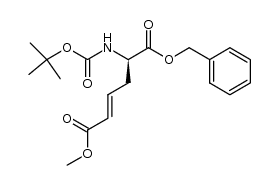 CAS#:115573-11-0
CAS#:115573-11-0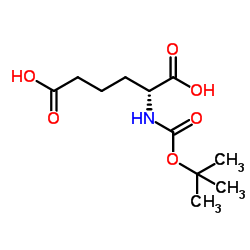 CAS#:110544-97-3
CAS#:110544-97-3 CAS#:14258-23-2
CAS#:14258-23-2 CAS#:72002-30-3
CAS#:72002-30-3
