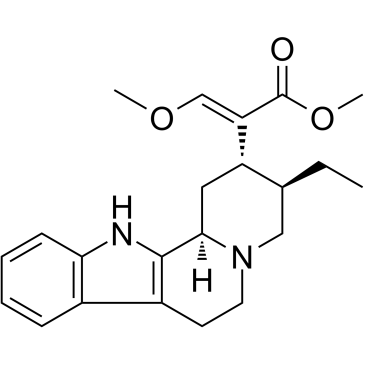
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
VS3660000
-
CHEMICAL NAME :
-
17,18-Seco-3-beta-yohimban-16-carboxylic acid, 16,17-didehydro-17-methoxy-, methyl ester, (E)-
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
7729-23-9
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
198909
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
2
-
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C22-H28-N2-O3
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
368.52
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
110 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - somnolence (general depressed activity) Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - other changes
-
REFERENCE :
-
NYKZAU Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. (Nippon Yakuri Gakkai, c/o Kyoto Daigaku Igakubu Yakurigaku Kyoshitsu, Konoe-cho, Yoshida, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606, Japan) V.40- 1944- Volume(issue)/page/year: 94,17,1989
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LD50 - Lethal dose, 50 percent kill
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intravenous
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
35 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Behavioral - somnolence (general depressed activity) Behavioral - convulsions or effect on seizure threshold Lungs, Thorax, or Respiration - other changes
-
REFERENCE :
-
NYKZAU Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. (Nippon Yakuri Gakkai, c/o Kyoto Daigaku Igakubu Yakurigaku Kyoshitsu, Konoe-cho, Yoshida, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606, Japan) V.40- 1944- Volume(issue)/page/year: 94,17,1989
|