Di-potassium monohydrogen phosphate
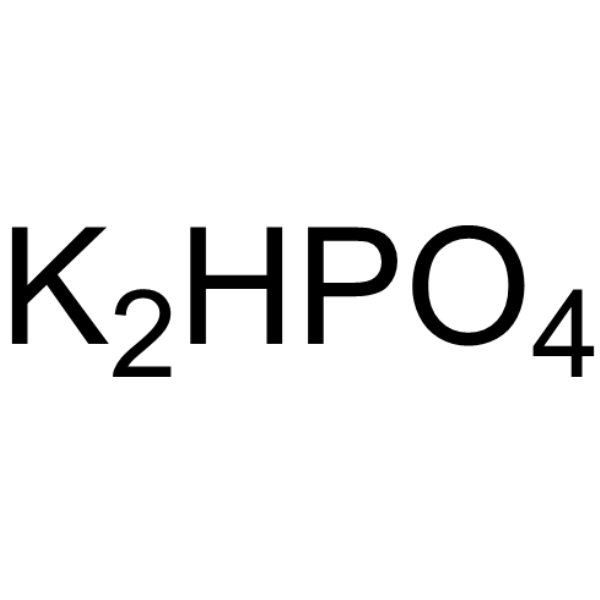
Di-potassium monohydrogen phosphate structure
|
Common Name | Di-potassium monohydrogen phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7758-11-4 | Molecular Weight | 174.18 | |
| Density | 2,44 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 158ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | HK2O4P | Melting Point | 340 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Di-potassium monohydrogen phosphateDipotassium hydrogen phosphate is a highly water-soluble salt which is often used as a fertilizer, food additive and buffering agent. Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate can be used as an excipient, such as pH regulator, buffer. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs[1][2]. |
| Name | Dipotassium hydrogenphosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate is a highly water-soluble salt which is often used as a fertilizer, food additive and buffering agent. Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate can be used as an excipient, such as pH regulator, buffer. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 2,44 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 158ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 340 °C |
| Molecular Formula | HK2O4P |
| Molecular Weight | 174.18 |
| Exact Mass | 173.888657 |
| PSA | 93.23000 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Hygroscopic. |
| Water Solubility | 1600 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi, C, T, F |
| Risk Phrases | 36-35-22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25-S36-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | TC8450000 |
| HS Code | 2835240000 |
| HS Code | 2835240000 |
|---|
|
A synthetic O2 -tolerant butanol pathway exploiting native fatty acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112(1) , 120-8, (2014) Several synthetic metabolic pathways for butanol synthesis have been reported in Escherichia coli by modification of the native CoA-dependent pathway from selected Clostridium species. These pathways ... |
|
|
Glucose and glycerol concentrations and their tracer enrichment measurements using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Mass Spectrom. 49(10) , 980-8, (2014) The present study describes a new liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for high-throughput quantification of glucose and glycerol in human plasma using stable isotopically labeled int... |
|
|
Ultrastructural morphologic changes in mycobacterial biofilm in different extreme condition.
Ultrastruct. Pathol. 39(1) , 38-48, (2015) The aim of this study was to investigate the morphologic and ultrastructural features of biofilms of slow and fast-growing mycobacteria in different stress conditions, presence and absence of oleic ac... |
| Mediject P |
| DKP |
| dipotassium-o-phosphate |
| Di-PotassiumPhosphateAr |
| MFCD00011383 |
| Potassium hydrogen phosphate (2:1:1) |
| Isolyte |
| DIPOTASSIUM PHOSPHATE |
| phosphate dipotassium |
| EINECS 231-834-5 |
| SEC-POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE |
| POTASSIUM BIPHOSPHATE |
| dikaliumphosphate |
| Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate |
| POTASSIUM MONOPHOSPHATE |

