Bopindolol fumarate
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 10:21:58
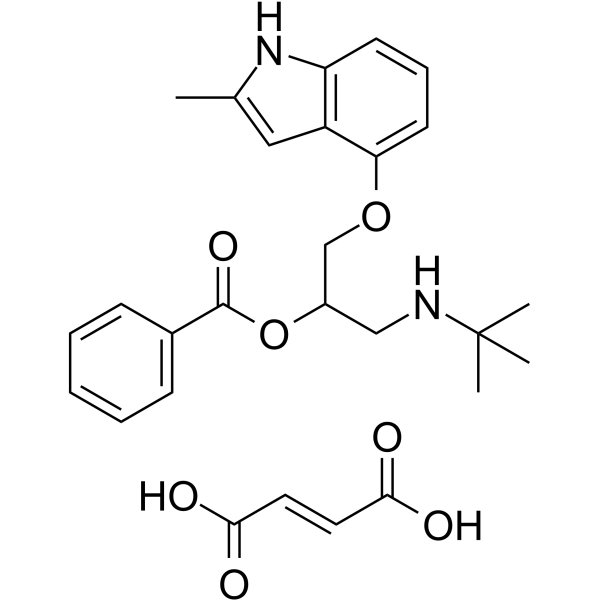
Bopindolol fumarate structure
|
Common Name | Bopindolol fumarate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79125-22-7 | Molecular Weight | 496.55 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32N2O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Bopindolol fumarateBopindolol ((±)-Bopindolol) fumarate is an orally active antagonist of β-adrenoceptors (ARs) with partial agonist activity. Bopindolol fumarate is non-selective for β1- and β2-ARs and has low affinity for β3-AR subtype. Bopindolol fumarate is a prodrug of pindolol and can be used for essential and renovascular hypertension research[1][2]. |
| Name | Bopindolol fumarate |
|---|
| Description | Bopindolol ((±)-Bopindolol) fumarate is an orally active antagonist of β-adrenoceptors (ARs) with partial agonist activity. Bopindolol fumarate is non-selective for β1- and β2-ARs and has low affinity for β3-AR subtype. Bopindolol fumarate is a prodrug of pindolol and can be used for essential and renovascular hypertension research[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
β1 adrenoceptor β2 adrenoceptor β3 adrenoceptor |
| In Vivo | Bopindolol (intravenous injection; l8, 16 and 32 μg/kg) fumarate causes a dose-dependent inhibition of isoprenaline-induced tachycardia, and this agent is 4 times more potent than propranolol in anaesthetised dogs[1]. Bopindolol (intraperitoneal injection; 3.0 mg/kg) fumarate reduces the diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in pithed rats. And pindolol (1.0 mg/kg) produces similar decreases in DBP of about 8 mmHg. it also produces a dose-dependent decrease in heart rate[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32N2O7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 496.55 |
| InChIKey | SRGXLPJWUNBTKJ-WLHGVMLRSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1cc2c(OCC(CNC(C)(C)C)OC(=O)c3ccccc3)cccc2[nH]1.O=C(O)C=CC(=O)O |