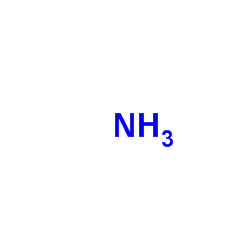
H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH
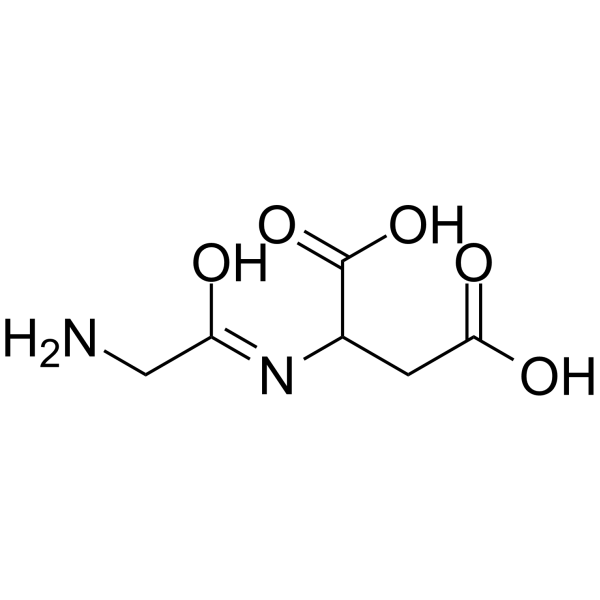
H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79731-35-4 | Molecular Weight | 190.15400 | |
| Density | 1.499 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 468.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O5 | Melting Point | 199-202℃ | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 237.3ºC | |
Use of H-Gly-DL-Asp-OHGlycyl-DL-aspartic acid (Gly-DL-Asp) is an aspartate derivative that can be used for amino acids synthesis[1]. |
| Name | Glycyl-DL-aspartic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Glycyl-DL-aspartic acid (Gly-DL-Asp) is an aspartate derivative that can be used for amino acids synthesis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.499 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 468.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 199-202℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 190.15400 |
| Flash Point | 237.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 190.05900 |
| PSA | 129.72000 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|
~93% 
H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH CAS#:79731-35-4 |
| Literature: Greenlee, William J.; Thorsett, Eugene D. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1981 , vol. 46, p. 5351 - 5353 |
|
~% 
H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH CAS#:79731-35-4 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , vol. 375, p. 182 |
|
~% 
H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH CAS#:79731-35-4 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , vol. 375, p. 182 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Purification, characterization, and localization of aspartoacylase from bovine brain.
J. Neurochem. 56(1) , 129-35, (1991) Canavan disease, an autosomal recessive disorder, is characterized biochemically by N-acetylaspartic aciduria and aspartoacylase (N-acyl-L-aspartate amidohydrolase; EC 3.5.1.15) deficiency. However, t... |
|
|
Conformation and structure of acidic dipeptides. Crystal structure of glycyl-L-aspartic acid dihydrate.
Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 19(2) , 206-11, (1982) The crystal structure of the acidic dipeptide glycyl-L-aspartic acid dihydrate, Gly-L-Asp X 2H2O, C6H10N2O5 X 2H2O, has been determined by means of three-dimensional counter X-ray data. The dipeptide ... |
|
|
Reduction of vanadium(V) to vanadium(IV) by NADPH, and vanadium(IV) to vanadium(III) by cysteine methyl ester in the presence of biologically relevant ligands.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1770(8) , 1212-8, (2007) To better understand the mechanism of vanadium reduction in ascidians, we examined the reduction of vanadium(V) to vanadium(IV) by NADPH and the reduction of vanadium(IV) to vanadium(III) by L-cystein... |
| h-gly-dl-asp-oh h2o |
| MFCD00066049 |
| H-Gly-DL-Asp-OH |
![2-[(2-chloroacetyl)amino]butanedioic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/493/67036-33-3.png)