Azithromycin
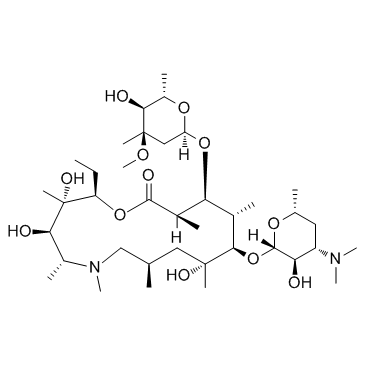
Azithromycin structure
|
Common Name | Azithromycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 83905-01-5 | Molecular Weight | 748.984 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 822.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C38H72N2O12 | Melting Point | 113-115°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 451.0±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of AzithromycinAzithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. |
| Name | azithromycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Azithromycin (2 μM) augments rhinovirus-induced IFNβ expression in primary bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatics, which is associated with over-expression of RIG-I like receptors and repression of viral replication. Knockdown of MDA5, but not knockdown of RIG-I, diminishes azithromycin (2 μM)-enhanced viral-induced IFNβ expression in asthmatic primary bronchial epithelial cells[1]. Azithromycin specifically reduces MMP-9 mRNA and protein levels without affecting NF-κB in endotoxin-challenged monocytic THP-1 cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Azithromycin (50 mg/kg) has no effect on bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory parameters and LDH levels in a mouse model of asthma exacerbation. Azithromycin induces neither general inflammatory parameters nor LDH release in a mouse model of asthma exacerbation, and augments expression of interferon-stimulated genes and the pattern recognition receptor MDA5 but not RIG-I in exacerbating mice[1]. |
| Cell Assay | THP-1 cells (106 cells in 1 mL RPMI medium, without antibiotics, growth factors or serum) are seeded in each well of 24-well plates and allowed to settle for 1 hour. Next, 50 μL of the test compound is added followed by 50 μL of LPS (final concentration of 10 μg/mL). After 24h (37°C and 5% CO2) the supernatants and cell pellets are collected (1200 rpm, 5 min). THP-1 cell viability is tested using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT). MTT is dissolved at 2 mg/mL in PBS and aliquots are stored at -20°C. The MTT assay is performed according to the suppliers instructions. Absorbance of MTT converted into formazan is measured at a wavelength of 570 nm with background subtraction at 630 nm. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 822.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 113-115°C |
| Molecular Formula | C38H72N2O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 748.984 |
| Flash Point | 451.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 748.508545 |
| PSA | 180.08000 |
| LogP | 3.33 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.537 |
| InChIKey | MQTOSJVFKKJCRP-ZOFOWXHFSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC1OC(=O)C(C)C(OC2CC(C)(OC)C(O)C(C)O2)C(C)C(OC2OC(C)CC(N(C)C)C2O)C(C)(O)CC(C)CN(C)C(C)C(O)C1(C)O |
| Storage condition | Store at -20°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | RN6960000 |
| HS Code | 2941500000 |
|
~88% 
Azithromycin CAS#:83905-01-5 |
| Literature: KOPRAN RESEARCH LABORATORIES LTD Patent: WO2007/15265 A2, 2007 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 12-13 ; |
|
~89% 
Azithromycin CAS#:83905-01-5 |
| Literature: Kim, Hyoung Cheul; Kang, Sung Ho Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, 2009 , vol. 48, # 10 p. 1827 - 1829 |
|
~% 
Azithromycin CAS#:83905-01-5 |
| Literature: WO2007/80507 A2, ; Page/Page column 12 ; |
|
~% 
Azithromycin CAS#:83905-01-5 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 53, # 50 p. 16923 - 16944 |
| HS Code | 2941500000 |
|---|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation and Persistence, along with the Production of Quorum Sensing-Dependent Virulence Factors, Are Disrupted by a Triterpenoid Coumarate Ester Isolated from Dalbergia trichocarpa, a Tropical Legume.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0132791, (2015) Recently, extracts of Dalbergia trichocarpa bark have been shown to disrupt P. aeruginosa PAO1 quorum sensing (QS) mechanisms, which are key regulators of virulence factor expression and implicated in... |
|
|
Macrolides rapidly inhibit red blood cell invasion by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.
BMC Biol. 13 , 52, (2015) Malaria invasion of red blood cells involves multiple parasite-specific targets that are easily accessible to inhibitory compounds, making it an attractive target for antimalarial development. However... |
|
|
Purification and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacillithiol transferase BstA.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(9) , 2851-61, (2014) Gram-positive bacteria in the phylum Firmicutes synthesize the low molecular weight thiol bacillithiol rather than glutathione or mycothiol. The bacillithiol transferase YfiT from Bacillus subtilis wa... |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-15-oxo-11-{[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-b-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-13-yl 2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranoside |
| 6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranoside |
| N-Methyl-11-aza-10-deoxo-10-dihydroerythromycin A |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-11-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-13-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-on |
| Azithromycin |
| Ribotrex |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-15-oxo-11-{[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-b-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-13-yl 2, |
| 2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranoside |
| MFCD00873574 |
| Tobil |
| Zistic |
| Azithral |
| Arzomicin |
| Zithromac |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-15-oxo-11-{[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-13-yl |
| xz405 |
| Aztrin |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-11-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-13-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one |
| Setron |
| 1-Oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one, 13-[(2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-b η-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-, (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)- |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-11-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(diméthylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-méthyltétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-2-éthyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-13-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-méthoxy-4,6-diméthyltétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptaméthyl-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadécan-15-one |
| Aruzilina |
| Zeto |
| 1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one, 13-[(2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-a-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-b-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-, (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)- |
| Azadose |
| Aziwok |
| Azimin |
| Azenil |
| 9-Deoxo-9a-methyl-9a-aza-9a-homoerythromycin A |
| azithromycinum [INN_la] |
| (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-2-Ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-15-oxo-11-{[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-13-yl 2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranoside |
| XZ-450 |
| Zifin |
| Ultreon |
| 1-Oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one, 13-[(2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-, (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)- |

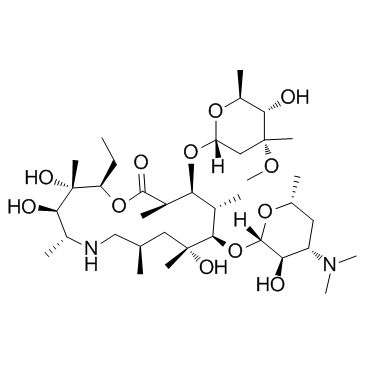
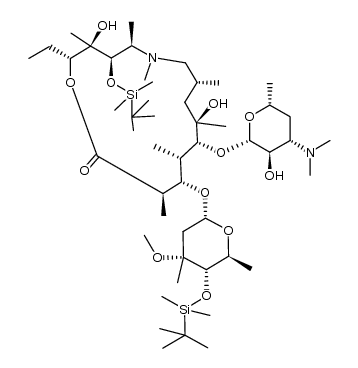

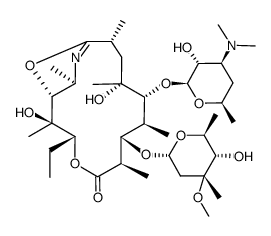
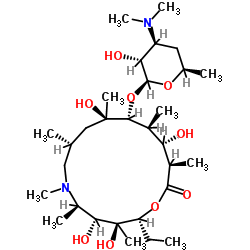 CAS#:117693-41-1
CAS#:117693-41-1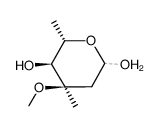 CAS#:18423-89-7
CAS#:18423-89-7 CAS#:172617-84-4
CAS#:172617-84-4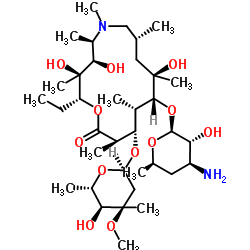 CAS#:612069-27-9
CAS#:612069-27-9
