SC-66
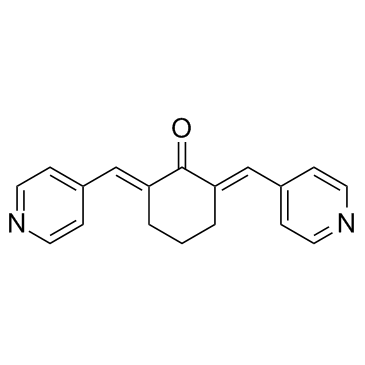
SC-66 structure
|
Common Name | SC-66 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 871361-88-5 | Molecular Weight | 276.332 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 514.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H16N2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 260.0±36.5 °C | |
Use of SC-66SC66 is a novel Akt inhibitor, reduces cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner, inhibits colony formation and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. |
| Name | 2,6-bis(pyridin-4-ylmethylidene)cyclohexan-1-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | SC66 is a novel Akt inhibitor, reduces cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner, inhibits colony formation and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Akt |
| In Vitro | SC66 inhibits cell viability and colony forming capacity of HCC cells with IC50s of 0.77,0.47,0.92,0.75 and 2.85 μg/mL at 72 hours for HepG2, Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5,HA22T/VGH and Huh7 cells. HepG2, HA22T/VGH and PLC/PRF/5 cells have similar IC50s of approximately 0.85 and 0.75 μg/mL at 48 and 72 hours, respectively. To determine whether the decrease in cell viability is related to apoptosis induction, TUNEL assays are performed in Hep3B and Huh7 cells treated with 1, 2 and 4 μg/mL of SC66 for 24 hours. In Hep3B cells the number of TUNEL-positive cells increased with increasing concentrations of SC66, whereas in Huh7 cells very few light brown-colored cells are observed only after treatment with 4 μg/mL SC66[1]. |
| In Vivo | To demonstrate the effectiveness in vivo of SC66 on HCC, a mouse xenograft tumor model of Hep3B cells is used. When tumors became palpable, at a size of about 150 mm3, mice are randomized into three groups of 6 animals each. The treated group receive SC66 at 15 and 25 mg/kg twice a week via i.p. injection, while the untreated group receive the vehicle alone. Treatment with 25 mg/Kg SC66 significantly reduces tumor volume to 37% on day 17 when compared with tumors of the untreated group[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells (5 ×103/well) are distributed into each well of 96-well microtiter plates and then incubated overnight. At time 0, the medium is replaced with fresh complete medium and different doses of SC66 are added. Cells are cultured for 24, 48 and 72 hours. At the end of treatment, MTS assays are performed using the CellTiter Aqueous OneSolution kit. Cell viability is expressed as a percentage of the absorbance measured in the control cells. Values are expressed as means±SD of three separate experiments, each performed in triplicate[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Male nude athymic mice (Fox1 nu/nu) aged 4 weeks are used. Suspensions of 1×107 Hep3B cells in 0.2 mL of PBS are inoculated into the right flank of the animal. When tumors became palpable (around 150 mm3), the mice are randomly divided into three groups of 6 animals each, with the various tumor volumes equally distributed among the three groups. Two groups of mice are treated twice a week with 15 and 25 mg/kg SC66 suspended in DMSO, further diluted in a solution of 25% ethanol and administered via i.p. injection. The control group receive the vehicle alone. Tumor volumes are determined twice a week using calipers. Primary tumor volumes are calculated. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 514.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H16N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 276.332 |
| Flash Point | 260.0±36.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 276.126251 |
| PSA | 42.85000 |
| LogP | 3.03 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.683 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
Cytotoxic activity of the novel small molecule AKT inhibitor SC66 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Oncotarget 6(3) , 1707-22, (2015) Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is characterized by limited response to current drug therapies. Here, we report that SC66, a novel AKT inhibitor, reduced cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent ma... |
|
|
p22phox confers resistance to cisplatin, by blocking its entry into the nucleus.
Oncotarget 6(6) , 4110-25, (2015) Cisplatin (CDDP) is a potent chemotherapeutic agent but resistance to the drug remains a major challenge in cancer treatment. To evaluate the efficacy of CDDP in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), w... |
|
|
PCNA-interacting peptides reduce Akt phosphorylation and TLR-mediated cytokine secretion suggesting a role of PCNA in cellular signaling.
Cell. Signal. 27 , 1478-87, (2015) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), commonly known as a nuclear protein essential for regulation of DNA replication, DNA repair, and epigenetics, has recently been associated with multiple cyto... |
| Cyclohexanone, 2,6-bis(4-pyridinylmethylene)-, (2E,6E)- |
| (2E,6E)-2,6-Bis(4-pyridinylmethylene)cyclohexanone |
| SC-66 |
| SC66 |