D-2-Phenylglycine
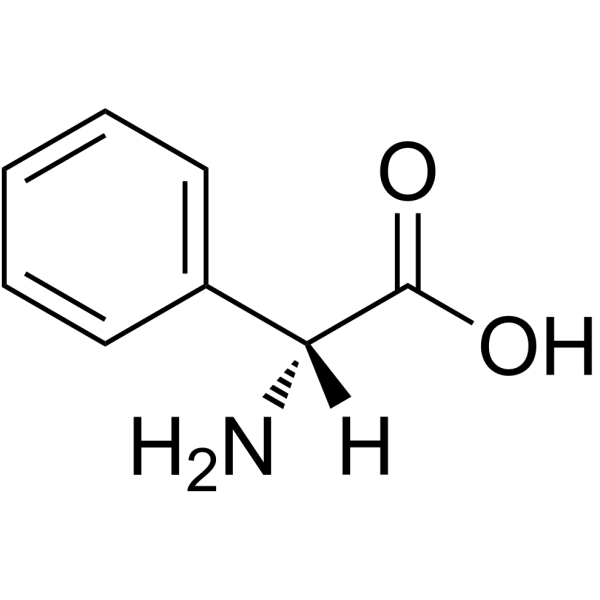
D-2-Phenylglycine structure
|
Common Name | D-2-Phenylglycine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 875-74-1 | Molecular Weight | 151.163 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 288.7±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H9NO2 | Melting Point | 302ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 128.4±24.0 °C | |
Use of D-2-PhenylglycineH-D-Phg-OH is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
| Name | D-α-phenylglycine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-D-Phg-OH is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 288.7±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 302ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H9NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 151.163 |
| Flash Point | 128.4±24.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 151.063324 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 0.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.589 |
| InChIKey | ZGUNAGUHMKGQNY-SSDOTTSWSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(C(=O)O)c1ccccc1 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Glyphosate suppresses the antagonistic effect of Enterococcus spp. on Clostridium botulinum.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16 , 1138-41, (2006) During the last 10-15 years, an increase of Clostridium botulinum associated diseases in cattle has been observed in Germany. The reason for this development is currently unknown. The normal intestina... |
|
|
Two plate-based colorimetric assays for screening α-amino acid ester hydrolase with high synthesis/hydrolysis ratio.
Enzyme Microb. Technol. 51(2) , 107-12, (2012) α-Amino acid ester hydrolases (AEHs) are enzymes of interest to the semi-synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics with α-amino, such as cephalexin and cefaclor. An undesired side reaction, the hydrolysis of ... |
|
|
Mutation-specific potency and efficacy of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channel potentiators.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 330(3) , 783-91, (2009) Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) Cl(-) channel. The mutations G551D and G1349D, which affect the nucleotide-binding domains... |
| H-L-PHG-OH |
| D-(−)-α-Phenylglycine |
| MFCD00008061 |
| (R)-phenylglycine |
| H-DL-Phg-OH |
| 2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid |
| (S)-(+)-α-Phenylglycine |
| L(+)-alpha-Phenylglycine |
| (2S)-Amino(phenyl)acetic acid |
| D-(-)-α-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| DL-α-Phenylglycine |
| (R)-2-phenylglycine |
| alpha-phenylglycine |
| RARECHEM AK ML 0501 |
| Benzeneacetic acid, α-amino-, (S)- |
| L-alpha-phenylglycine |
| (2R)-Amino(phenyl)acetic acid |
| (2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetic acid |
| L-α-phenylglycine |
| (R)-(−)-2-Phenylglycine |
| (R)-(-)-α-aminophenylacetic acid |
| Benzeneacetic acid, α-amino-, (αS)- |
| (2S)-amino(phenyl)ethanoic acid |
| EINECS 212-876-3 |
| (S)-(+)-α-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| L-(+)-2-Phenylglycine |
| L-Aminophenyl |
| (R)-(-)-2-Phenylglycine |
| 2-phenylglycine |
| DL-PHENYLGLYCINE |
| Phenylglycine |
| (S)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid |
| (R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid |
| DL-A-PHENYLGLYCINE |
| S-(+)-α-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| (S)-(+)-2-Phenylglycine |
| DL-Alpha-Phenylglycine |
| L-(+)-alpha-Phenylglycine |
| H-PHG-OH |
| (±)-α-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| PHENYLGLYCINE-L-2 |
| DL-2-PHENYLGLYCINE |
| L-(+)-α-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| (+/-)-Alpha-Aminophenylacetic Acid |
| L-(+)-α-phenylglycine |
| L-Phenylglycine |
| D-alpha-phenylglycine |
| DL-.α.-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| Benzeneacetic acid, α-amino-, (αR)- |
| 2-Phenyl-DL-glycine |
| D−(−)-α-Phenylglycine |
| L-2-PHENYLGLYCINE |
| (R)-(−)-α-Aminophenylacetic acid |
| (S)-phenylglycine |
| L(+)-α-Phenylglycine |
| L−(+)-α-Phenylglycine |
| (R)-α-Aminobenzeneacetic acid |
| H-D-Phg-OH |
| Ampicillin Impurity 12 |
 CAS#:29125-25-5
CAS#:29125-25-5 CAS#:367260-42-2
CAS#:367260-42-2 CAS#:104266-89-9
CAS#:104266-89-9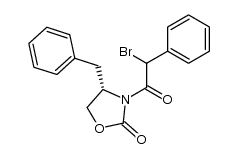 CAS#:113543-39-8
CAS#:113543-39-8 CAS#:113543-46-7
CAS#:113543-46-7 CAS#:2835-06-5
CAS#:2835-06-5 CAS#:24461-61-8
CAS#:24461-61-8 CAS#:100-52-7
CAS#:100-52-7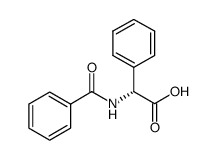 CAS#:10419-67-7
CAS#:10419-67-7![2-{[(4-Methylphenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-2-phenylacetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/267/60712-47-2.png) CAS#:60712-47-2
CAS#:60712-47-2 CAS#:4870-65-9
CAS#:4870-65-9 CAS#:39878-87-0
CAS#:39878-87-0 CAS#:497-19-8
CAS#:497-19-8 CAS#:83649-47-2
CAS#:83649-47-2 CAS#:85711-13-3
CAS#:85711-13-3 CAS#:90319-52-1
CAS#:90319-52-1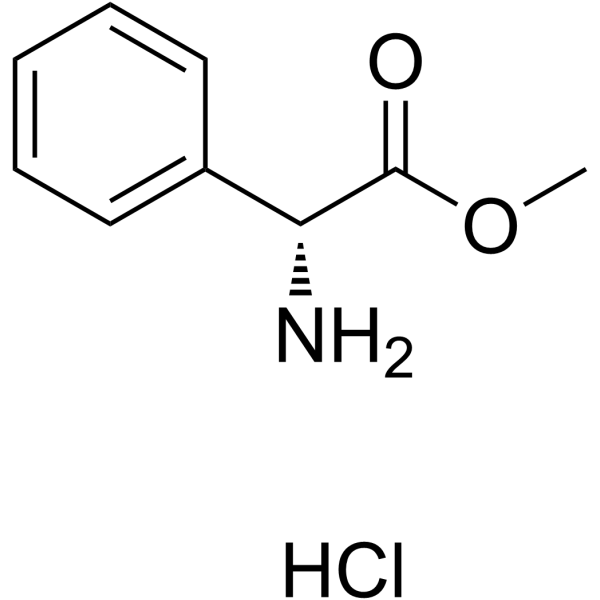 CAS#:19883-41-1
CAS#:19883-41-1 CAS#:15028-39-4
CAS#:15028-39-4
