Diprotin A
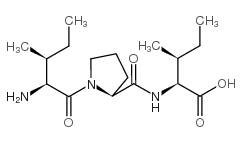
Diprotin A structure
|
Common Name | Diprotin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90614-48-5 | Molecular Weight | 341.44600 | |
| Density | 1.14 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 583.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H31N3O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 306.5ºC | |
Use of Diprotin ADiprotin A (Ile-Pro-Ile) is an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV)[1]. |
| Name | diprotin a |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diprotin A (Ile-Pro-Ile) is an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: DPP-IV[1] |
| In Vitro | Diprotin A (100 μM; 30 minutes after CXCR4-blocker or Src-inhibitor treatment) induces the phosphorylation of Src [Tyr 416] and VE-cadherin [Tyr731] in hECs in both normoxia and H/R conditions in human endothelial cells and disrupts endothelial cell-to-cell junctions, which are attenuated by CXCR4 (receptor of SDF-1α)-blocker or Src-inhibitor[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Human endothelial cells[1] Concentration: 100 μM Incubation Time: 30 minutes after CXCR4-blocker or Src-inhibitor treatment Result: Induced the phosphorylation of Src [Tyr 416] and VE-cadherin [Tyr731] in hECs. |
| In Vivo | Diprotin A (intraperitoneal injection; 70 μg/kg; twice daily; 7 days) increases the phosphorylation of Src and VE-cadherin and aggravates vascular leakage in the retinas. Collectively, Diprotin A induces vascular leakage by augmenting the SDF-1α/CXCR4/Src/VE-cadherin signaling pathway[1]. Animal Model: Streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy model in wild-type C57/BL6 mice[1] Dosage: 70 μg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; twice daily; 7 days Result: Induced vascular leakage by augmenting the SDF-1α/CXCR4/Src/VE-cadherin signaling pathway. |
| References |
| Density | 1.14 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 583.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H31N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 341.44600 |
| Flash Point | 306.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 341.23100 |
| PSA | 112.73000 |
| LogP | 1.99540 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.517 |
| InChIKey | JNTMAZFVYNDPLB-PEDHHIEDSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(N)C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC(C(=O)O)C(C)CC |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NR4737000 |
|
In vitro assessment of the multifunctional bioactive potential of Alaska pollock skin collagen following simulated gastrointestinal digestion.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(7) , 1514-20, (2015) Dietary mineral deficiency, hypertension and diabetes have become serious human health problems. Dietary approaches are increasingly being investigated to address these issues. Identification of food-... |
|
|
Antidiabetic property of Symplocos cochinchinensis is mediated by inhibition of alpha glucosidase and enhanced insulin sensitivity.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e105829, (2014) The study is designed to find out the biochemical basis of antidiabetic property of Symplocos cochinchinensis (SC), the main ingredient of 'Nisakathakadi' an Ayurvedic decoction for diabetes. Since di... |
|
|
Utilisation of the isobole methodology to study dietary peptide-drug and peptide-peptide interactive effects on dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibition.
Food Funct. 6(1) , 313-20, (2015) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) is used as a means to regulate post-prandial serum glucose in type 2 diabetics. The effect of drug (Sitagliptin®)/peptide and binary peptide mixtures on ... |
| MFCD00038707 |
| H-ILE-PRO-ILE-OH |
| ILE-PRO-ILE H2O |
| Ile-Pro-Ile-OH |
| H-ILE-PRO-ILE-OH H2O |
| DIPEPTIDYLPEPTIDASE IV INHIBITOR I |
| L-Isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-isoleucine |
| ILE-PRO-ILE |
| L-Ile-L-Pro-L-Ile-OH |