Sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696)
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 09:18:37
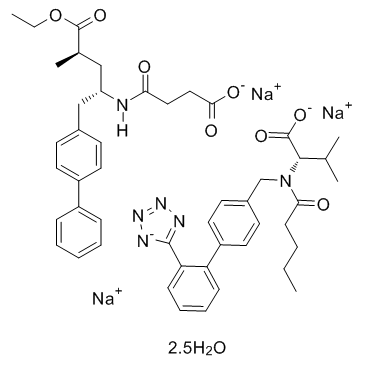
Sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) structure
|
Common Name | Sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 936623-90-4 | Molecular Weight | 957.99 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C48H60N6Na3O10.5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696)LCZ696 is a dual angiotensin II receptor and neprilysin inhibitor. |
| Name | lcz696 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | LCZ696 is a dual angiotensin II receptor and neprilysin inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | LCZ696 is a single molecule that is comprised of molecular moieties of valsartan, an ARB, and AHU377, a neprilysin inhibitor (1:1 ratio)[1]. |
| In Vivo | LCZ696 exerts a blood pressure lowering effect. Blood pressure reduction by LCZ696 is associated with a significant increase in urinary sodium excretion and sympathetic activity suppression. LCZ696 significantly ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy and inflammation, coronary arterial remodeling, and vascular endothelial dysfunction in high-salt loaded SHRcp compared with valsartan[1]. The neprilysin inhibitor component of LCZ696, LBQ657, inhibits hypertrophy but not fibrosis. The angiotensin receptor blocker component of LCZ696, valsartan inhibits both hypertrophy and fibrosis. Dual valsartan+LBQ augment the inhibitory effects of valsartan and the highest doses completely abrogate angiotensin II-mediated effects[2]. Pre-treatment with LCZ696 reduces the ischemic area. The decrease in cerebral blood flow in the peripheral region of the ischemic area is significantly attenuated by pre-treatment with LCZ696. LCZ696 pre-treatment significantly decreases the increase of superoxide anion production in the cortex on the ischemic side[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: LCZ696 or valsartan is orally administered as a powder in gelatin mini-capsules at the beginning of the dark period once daily. The vehicle group rats are given empty capsules. Miniature telemetry devices are implanted into 12 or 13-week-old SHRs. BP and heart rate variability, low frequency power of systolic BP, and spontaneous baroreceptor reflex gain are monitored during the dark and light periods. The SHRs are divided into 3 groups at 16 weeks of age: (i) vehicle, (ii) LCZ696, and (iii) valsartan. The dose of LCZ696 and valsartan is 20 and 10mg/kg/day from 16 to 18 weeks of age, respectively, and 60 and 30mg/kg/day from 18 to 23 weeks of age, respectively. At 21 weeks of age, the SHR diet is switched to a low-salt diet from a high-salt diet[1]. Mice: Mice are treated with VAL (3 mg/kg per day) or LCZ696 (6 mg/kg per day) orally as powder in gelatin mini-capsules daily for 2 weeks before MCA occlusion. Body weight is measured after VAL or LCZ696 pre-treatment for 2 weeks. Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and heart rate are measured by telemetry at 10 weeks of age[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C48H60N6Na3O10.5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 957.99 |
| PSA | 207.53000 |
| LogP | 5.34730 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Valsartan |
| Sodium 4-{[(2S,4R)-1-(4-biphenylyl)-5-ethoxy-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-pentanyl]amino}-4-oxobutanoate (2S)-3-methyl-2-(pentanoyl{[2'-(tetrazol-1-id-5-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}amino)butanoate hydrate (6:2:2:5) |
| Entresto |
| LCZ 696 |
| L-Valine, N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-, compd. with α-ethyl (αR,γS)-γ-[(3-carboxy-1-oxopropyl)amino]-α-methyl[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-pentanoate, sodium salt, hydrate (2:2:6:5) |
| trisodium [3-((1S,3R)-1-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl-3-ethoxycarbonyl-1-butylcarbamoyl)propionate-(S)-3-methyl-2-(pentanoyl{2”-(tetrazol-5-ylate)biphenyl-4-ylmethyl}amino)butyrate] hemipentahydrate |
| trisodium 3-((1S,3R)-1-(biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)-3-(ethoxycarbonyl)butylcarbamoyl)propionate (S)-3-methyl-2-(pentanoyl-(2-(tetrazol-1-at-5-yl)biphenyl-4'-ylmethyl)amino)butyrate hemipentahydrate |
| 3-(1-Biphenyl-4-ylMethyl-3-ethoxycarbonyl-1-butylcarbaMoyl)propionate-3'-Methyl-2'-(pentanoyl(2'-(tetrazol-5-ylate)biphenyl-4'-ylMethyl)aMino)butyrate |