2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline
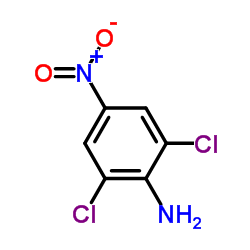
2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99-30-9 | Molecular Weight | 207.014 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 323.0±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2N2O2 | Melting Point | 187-192 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 149.1±26.5 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | dicloran |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 323.0±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 187-192 ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Cl2N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 207.014 |
| Flash Point | 149.1±26.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 205.964981 |
| PSA | 71.84000 |
| LogP | 3.54 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.656 |
| InChIKey | BIXZHMJUSMUDOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Nc1c(Cl)cc([N+](=O)[O-])cc1Cl |
| Water Solubility | 1 g/L (60 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300-H310-H330-H373-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P273-P280-P284-P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BX2975000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921420090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2921420090 aniline derivatives and their salts VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Application of the phylogenetic species concept to Wallemia sebi from house dust and indoor air revealed by multi-locus genealogical concordance.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0120894, (2015) A worldwide survey of Wallemia occurring in house dust and indoor air was conducted. The isolated strains were identified as W. sebi and W. muriae. Previous studies suggested that the W. sebi phylogen... |
|
|
Strontium exerts dual effects on calcium phosphate cement: Accelerating the degradation and enhancing the osteoconductivity both in vitro and in vivo.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 103(5) , 1613-21, (2015) Calcium phosphate cements (CPCs) have long been used as osteoconductive bone substitutes in the treatment of bone defects. However, the degradation rate of CPC is typically too slow to match the new b... |
|
|
Characterization and identification of an indirect cytochrome P-450-initiated denitrosation of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitroaniline in rat hepatic microsomes.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 95(1) , 139-52, (1988) The metabolism of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitroaniline (DCNA) to a unique denitrosated product, 3,5-dichloro-p-aminophenol (DCAP), was investigated in rat hepatic microsomes using an HPLC system containing a r... |
| 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitrobenzenamine |
| dicloran |
| 4-nitro-2,6-dichloroaniline |
| Botran |
| Benzenamine, 2,6-dichloro-4-nitro- |
| Resinan |
| DCNA |
| dichloran |
| ZR BG FG DNW |
| MFCD00007677 |
| 1-amino-2,6-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene |
| Bortran |
| 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline |
| bpe |
| 2,6-dichloro-p-nitroaniline |
| CNA |
| Ditranil |
| cdna |
| Allisan |
| Dicloran [BSI] |
| EINECS 202-746-4 |
 CAS#:100-01-6
CAS#:100-01-6 CAS#:22134-75-4
CAS#:22134-75-4 CAS#:1817-73-8
CAS#:1817-73-8 CAS#:507-40-4
CAS#:507-40-4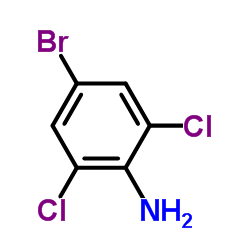 CAS#:697-88-1
CAS#:697-88-1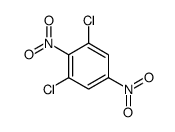 CAS#:13633-34-6
CAS#:13633-34-6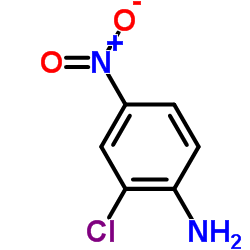 CAS#:121-87-9
CAS#:121-87-9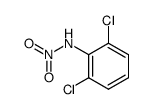 CAS#:54381-76-9
CAS#:54381-76-9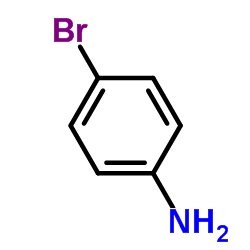 CAS#:106-40-1
CAS#:106-40-1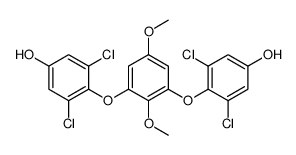 CAS#:141794-49-2
CAS#:141794-49-2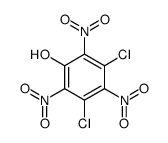 CAS#:19046-87-8
CAS#:19046-87-8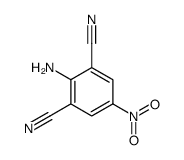 CAS#:20033-48-1
CAS#:20033-48-1![2-Thiazolamine,5-[2-(2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]-4-phenyl- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/187/26164-57-8.png) CAS#:26164-57-8
CAS#:26164-57-8 CAS#:118-75-2
CAS#:118-75-2 CAS#:20098-48-0
CAS#:20098-48-0 CAS#:626-43-7
CAS#:626-43-7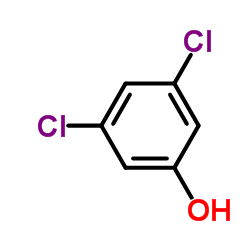 CAS#:591-35-5
CAS#:591-35-5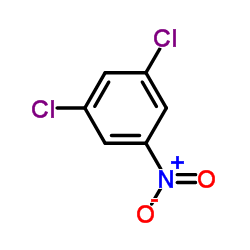 CAS#:618-62-2
CAS#:618-62-2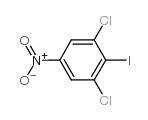 CAS#:62778-19-2
CAS#:62778-19-2
