
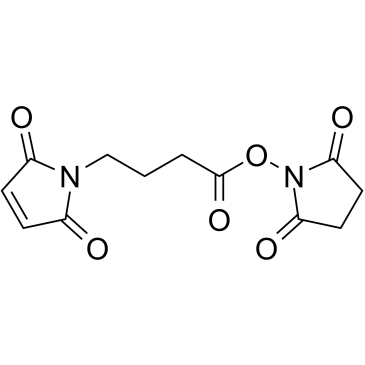
N-(4-马来酰亚胺丁酰基)琥珀酰亚胺结构式

|
常用名 | N-(4-马来酰亚胺丁酰基)琥珀酰亚胺 | 英文名 | gmbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 80307-12-6 | 分子量 | 280.233 | |
| 密度 | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 461.3±47.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C12H12N2O6 | 熔点 | 123-129ºC | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 232.8±29.3 °C |
|
Highly efficient capture and harvest of circulating tumor cells on a microfluidic chip integrated with herringbone and micropost arrays.
Biomed. Microdevices 17(2) , 39, (2015) Circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which are derived from primary tumor site and transported to distant organs, are considered as the major cause of metastasis. So far, various techniques have been applied for CTC isolation and enumeration. However, there exists... |
|
|
A chitosan coated monolith for nucleic acid capture in a thermoplastic microfluidic chip.
Biomicrofluidics 8(4) , 044109, (2014) A technique for microfluidic, pH modulated DNA capture and purification using chitosan functionalized glycidyl methacrylate monoliths is presented. Highly porous polymer monoliths are formed and subsequently functionalized off-chip in a batch process before i... |
|
|
Expansion of CTCs from early stage lung cancer patients using a microfluidic co-culture model.
Oncotarget 5(23) , 12383-97, (2015) The potential utility of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) to guide clinical care in oncology patients has gained momentum with emerging micro- and nanotechnologies. Establishing the role of CTCs in tumor progression and metastasis depends both on enumeration an... |
|
|
Investigation on the reaction conditions of Staphylococcus aureus sortase A for creating surface-modified liposomes as a drug-delivery system tool.
Anticancer Res. 34(8) , 4521-7, (2014) This study aimed to determine the preferred conditions for the transpeptidase reaction of sortase A from Staphylococcus aureus, for the purpose of creating functional liposomes useful for a drug-delivery system (DDS).His-tagged recombinant sortase A with 59 a... |
|
|
Comparison of antibody functionality using different immobilization methods.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 84(2) , 215-23, (2003) This study investigates the influence of antibody immobilization methods on antigen capture. Adsorption and two surface chemistries, an aminosilane chemistry and a common heterobifunctional crosslinker (N-gamma-maleimidobutyryloxy-succinimide ester, GMBS), we... |
|
|
Developing a programmed restriction endonuclease for highly specific DNA cleavage.
Nucleic Acids Res. 33(22) , 7039-47, (2005) Specific cleavage of large DNA molecules at few sites, necessary for the analysis of genomic DNA or for targeting individual genes in complex genomes, requires endonucleases of extremely high specificity. Restriction endonucleases (REase) that recognize DNA s... |
|
|
Conversion of proteins to diazeniumdiolate-based nitric oxide donors.
Bioconjug. Chem. 10 , 838-842, (1999) Michael reaction of the methoxymethyl-protected monodiazeniumdiolate of piperazine (MOM-PIPERAZI/NO) with 4-maleimidobutyric acid followed by its conversion to the N-hydroxy-succinimido ester produces a reagent capable of transferring the nitric oxide (NO)-do... |
|
|
Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the polyamine, spermine: immunocytochemical localization in rat tissues.
Histochemistry 102(5) , 397-404, (1994) Two monoclonal antibodies of types IgG2b and IgG2a, anti-spermine-(Spm)-1 (ASPM-1) and anti-Spm-2 (ASPM-2) respectively were found among five clones of murine monoclonal antibodies, which were raised against Spm conjugated with bovine serum albumin via the cr... |
|
|
Immunocytochemistry for vancomycin using a monoclonal antibody that reveals accumulation of the drug in rat kidney and liver.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56(11) , 5883-91, (2012) We prepared monoclonal antibodies against N-(γ-maleimidobutyryloxy)succinimide-conjugated vancomycin (VM). The monoclonal antibody was specific for conjugated or free VM. The monoclonal antibody enabled us to develop an immunocytochemical method for detecting... |
|
|
Enhanced delivery of exogenous peptides into the class I antigen processing and presentation pathway.
Infect. Immun. 70(6) , 3249-58, (2002) Current immunization strategies, using peptide or protein antigens, generally fail to elicit cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte responses, since these antigens are unable to access intracellular compartments where loading of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-... |