羟丙基甲基纤维素
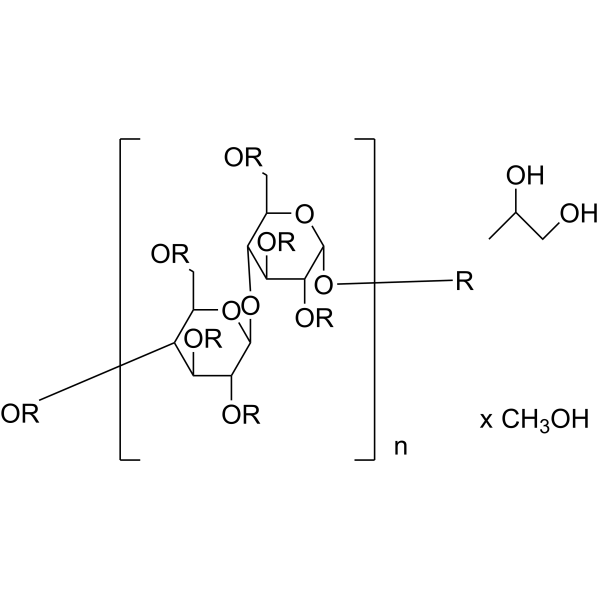
羟丙基甲基纤维素结构式

|
常用名 | 羟丙基甲基纤维素 | 英文名 | Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 9004-65-3 | 分子量 | 478.49 | |
| 密度 | 1.39 | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C18H38O14 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
Compounded preparations with nystatin for oral and oromucosal administration.
Acta Pol. Pharm. 70(4) , 759-62, (2013) Therapy of oral, esophageal and gastrointestinal candidiasis is still a common problem that can be solved by an administration of antimycotics. Major disadvantage of registered commercial antifungal medicinal products is their price, so the health care system... |
|
|
Curcumin amorphous solid dispersions: the influence of intra and intermolecular bonding on physical stability.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 19(8) , 976-86, (2014) We have investigated the physical stability of amorphous curcumin dispersions and the role of curcumin-polymer intermolecular interactions in delaying crystallization. Curcumin is an interesting model compound as it forms both intra and intermolecular hydroge... |
|
|
ROI-SCAVENGING ENZYME ACTIVITIES AS TOXICITY BIOMARKERS IN THREE SPECIES OF MARINE MICROALGAE EXPOSED TO MODEL CONTAMINANTS (COPPER, IRGAROL AND ATRAZINE)
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 104 , 294-301, (2014) There is a need to develop efficient tools to prevent damage to marine ecosystems due to pollution. Since microalgae play a key role in marine ecosystems, they are considered potentially useful for quick and sensitive toxicity bioassays. In this study an inte... |
|
|
Hepatic transcriptional analysis in rats treated with Cassia occidentalis seed: involvement of oxidative stress and impairment in xenobiotic metabolism as a putative mechanism of toxicity.
Toxicol. Lett. 229(1) , 273-83, (2014) The present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of Cassia occidentalis (CO) seeds on the transcriptional expression patterns of mRNAs in rat liver by microarray analysis. The results indicated that exposure of CO (0.5%) seeds in diet to rats differ... |
|
|
IKK2 inhibition using TPCA-1-loaded PLGA microparticles attenuates laser-induced choroidal neovascularization and macrophage recruitment.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0121185, (2015) The inhibition of NF-κB by genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of IKK2 significantly reduces laser-induced choroid neovascularization (CNV). To achieve a sustained and controlled intraocular release of a selective and potent IKK2 inhibitor, 2-[(ami... |
|
|
A new self-microemulsifying mouth dissolving film to improve the oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 39(9) , 1284-90, (2013) A new self-microemulsifying mouth dissolving film (SMMDF) for poorly water-soluble drugs such as indomethacin was developed by incorporating self-microemulsifying components with solid carriers mainly containing microcrystalline cellulose, low-substituted hyd... |
|
|
Formulation and drying of miconazole and itraconazole nanosuspensions.
Int. J. Pharm. 443(1-2) , 209-20, (2013) Miconazole and itraconazole possess adequate membrane permeability, but only slight water solubility, which limits their bioavailability and antifungal effect. To increase their dissolution rate, the compounds were nanoground by media milling to produce nanos... |
|
|
Note on the formulation of thermosensitive and mucoadhesive vaginal hydrogels containing the miniCD4 M48U1 as anti-HIV-1 microbicide.
Int. J. Pharm. 454(2) , 649-52, (2013) The miniCD4 M48U1 was formulated into thermosensitive and mucoadhesive pluronic(®) hydrogels as anti-HIV-1 microbicide. The release kinetics of M48U1 from F127/HPMC (20/1 wt%) and F127/F68/HPMC (22.5/2.5/1 wt%) studied during 24h by using Franz diffusion cell... |
|
|
Supersaturatable formulations for the enhanced oral absorption of sirolimus.
Int. J. Pharm. 445(1-2) , 108-16, (2013) The purpose of this study was to develop supersaturatable formulations for the enhanced solubility and oral absorption of sirolimus. Supersaturatable formulations of hydrophilic polymers and/or surfactants were screened by formulation screening, which is base... |
|
|
Improved human bioavailability of vemurafenib, a practically insoluble drug, using an amorphous polymer-stabilized solid dispersion prepared by a solvent-controlled coprecipitation process.
J. Pharm. Sci. 102(3) , 967-81, (2013) The present work deals with improving the solubility of vemurafenib, a practically insoluble drug, by converting it into an amorphous-solid dispersion using a solvent-controlled precipitation process. The dispersion containing vemurafenib and hypromellose ace... |