肌苷-5'-三磷酸三钠盐
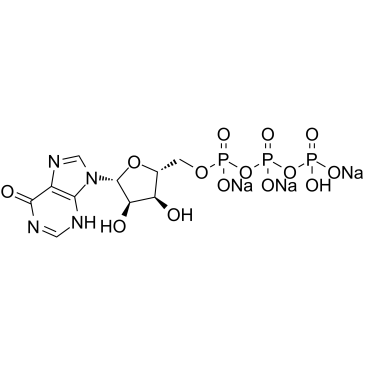
肌苷-5'-三磷酸三钠盐结构式

|
常用名 | 肌苷-5'-三磷酸三钠盐 | 英文名 | Inosine 5'-triphosphate (sodium salt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 35908-31-7 | 分子量 | 574.111 | |
| 密度 | 2.63g/cm3 | 沸点 | 994.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C10H12N4Na3O14P3 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 555.5ºC |
|
[Nucleoside-5'-triphosphate hydrolysis in the liver and kidney of rats with chronic alloxan diabetes].
Biomed. Khim. 52 , 364-369, (2006) Activity and some properties of a soluble enzyme hydrolyzing nucleoside-5'-triphosphates were studied in the liver and kidney of normal and diabetic rats. The enzyme activity was shown to be reduced by 34% (p < 0.01) in the liver extracts of diabetic animals,... |
|
|
Mapping interactions between the Ca2+-ATPase and its substrate ATP with infrared spectroscopy.
J. Biol. Chem. 278 , 10112-10118, (2003) Infrared spectroscopy has been used to map substrate-protein interactions: the conformational changes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase upon nucleotide binding and ATPase phosphorylation were monitored using the substrate ATP and ATP analogues (2'-d... |
|
|
Identification of an ITPase/XTPase in Escherichia coli by structural and biochemical analysis.
Structure 13 , 1511-1520, (2005) Inosine triphosphate (ITP) and xanthosine triphosphate (XTP) are formed upon deamination of ATP and GTP as a result of exposure to chemical mutagens and oxidative damage. Nucleic acid synthesis requires safeguard mechanisms to minimize undesired lethal incorp... |
|
|
Trinitrophenyl-ATP and -ADP bind to a single nucleotide site on isolated beta-subunit of Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. In vitro assembly of F1-subunits requires occupancy of the nucleotide-binding site on beta-subunit by nucleoside triphosphate.
J. Biol. Chem. 263 , 5569-5573, (1988) The stoichiometry of nucleotide binding to the isolated alpha- and beta-subunits of Escherichia coli F1-ATPase was investigated using two experimental techniques: (a) titration with fluorescent trinitrophenyl (TNP) derivatives of AMP, ADP, and ATP and (b) the... |
|
|
Distinct interactions of G(salpha-long), G(salpha-short), and G(alphaolf) with GTP, ITP, and XTP.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 64 , 583-593, (2002) The G(s)-proteins G(salpha-short) (G(salphaS)) and G(salpha-long) (G(salphaL)), and the olfactory G(s) protein (G(alphaolf)) mediate activation of adenylyl cyclase by the beta(2)-adrenoceptor (beta(2)AR). Early studies showed that the purine nucleotides GTP, ... |
|
|
Characterization of an ecto-ATPase activity in Cryptococcus neoformans.
FEMS Yeast Res. 5 , 899-907, (2005) Cryptococcus neoformans is the causative agent of pulmonary cryptococcosis and cryptococcal meningoencephalitis, which are major clinical manifestations in immunosuppressed patients. In the present study, a surface ATPase (ecto-ATPase) was identified in C. ne... |
|
|
Calcium ion-insensitive contraction of glycerinated porcine cardiac muscle fibers by Mg-inosine triphosphate. ITP as a tool to dissociate the contraction mechanism from the regulatory mechanism.
Circ. Res. 49(6) , 1350-5, (1981) The contraction of cardiac muscle that has been treated with glycerol requires Ca2+ (pCa 8-5), when MgATP is used as a substrate. In contrast, this preparation contracts, even in the absence of Ca2+ (pCa 8-10), when ATP is replaced by ITP. Ca2+ dependency was... |
|
|
Adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase: kinetic mechanism for the bovine skeletal muscle catalytic subunit.
Biochemistry 21(23) , 5794-9, (1982)
|
|
|
Conformational modification of muscle phosphofructokinase from Jaculus orientalis upon ligand binding.
FEBS Lett. 245(1-2) , 30-4, (1989) Phosphofructokinase from Jaculus orientalis muscle is an allosteric enzyme regulated by substrates and nucleotide effectors. The conformational modifications upon ligand binding were probed by UV difference spectra and reactivities of thiol groups towards dit... |
|
|
Diffusion limited component of mitochondrial F1-ATPase.
Int. J. Biochem. 25(5) , 701-6, (1993) 1. The possibility that the rate of ATP hydrolysis by F1-ATPase approaches the diffusion-controlled limits was investigated by measuring the values of kcat and kl (kcat/Km) as a function of increasing viscosity. 2. The values of kcat/Km decrease significantly... |